Page 233 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 233
Microeconomic Theory
Notes and gets all the income of customer. In this condition, the average revenue curve is a rectangular
hyperbola. It means that the total revenue by selling the product would be same whether the monopolist
decides any price of product. So all the points of AR curve are equal to each other in below region. So
the marginal revenue line (MR curve) is indicated by axis OX. In Fig. 11.3, it is shown that AR curve is a
Rectangular Hyperbola. Suppose that consumer has 8. When monopolist decides the price of product
as 4, as shown by point P, two units of product have been sold means total income is 8. In contrast
when monopoly lessens the price of product and makes it as 3, then point N shows that 4 units of
products have been sold. So the total income would be 8. This also indicates that the marginal revenue
for second product would be zero. In this figure OX-axis is MR Curve.
11.6 Graphical or Geometrical Relation between Total
Average and Marginal Revenues
There is following relation of a firm’s Total, Average and Marginal Revenues:
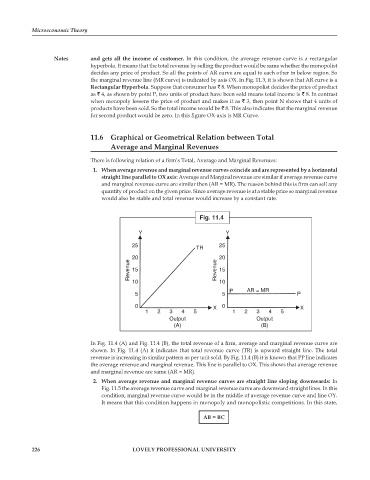
1. When average revenue and marginal revenue curves coincide and are represented by a horizontal
straight line parallel to OX axis: Average and Marginal revenue are similar if average revenue curve
and marginal revenue curve are similar then (AR = MR). The reason behind this is firm can sell any
quantity of product on the given price. Since average revenue is at a stable price so marginal revenue
would also be stable and total revenue would increase by a constant rate.
Fig. 11.4
Y Y
25 25
TR
20 20
Revenue 15 Revenue 15
10 10
P AR = MR
5 5 P
0 X 0 X
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
Output Output
(A) (B)
In Fig. 11.4 (A) and Fig. 11.4 (B), the total revenue of a firm, average and marginal revenue curve are
shown. In Fig. 11.4 (A) it indicates that total revenue curve (TR) is upward straight line. The total
revenue is increasing in similar pattern as per unit sold. By Fig. 11.4 (B) it is known that PP line indicates
the average revenue and marginal revenue. This line is parallel to OX. This shows that average revenue
and marginal revenue are same (AR = MR).
2. When average revenue and marginal revenue curves are straight line sloping downwards: In
Fig. 11.5 the average revenue curve and marginal revenue curve are downward straight lines. In this
condition, marginal revenue curve would be in the middle of average revenue curve and line OY.
It means that this condition happens in monopoly and monopolistic competitions. In this state,
AB = BC
226 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY