Page 237 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 237
Microeconomic Theory
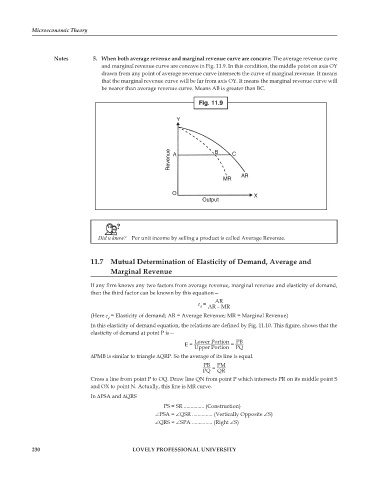
Notes 5. When both average revenue and marginal revenue curve are concave: The average revenue curve
and marginal revenue curve are concave in Fig. 11.9. In this condition, the middle point on axis OY
drawn from any point of average revenue curve intersects the curve of marginal revenue. It means
that the marginal revenue curve will be far from axis OY. It means the marginal revenue curve will
be nearer than average revenue curve. Means AB is greater than BC.
Fig. 11.9
Y
Revenue A B C
AR
MR
O X
Output
Per unit income by selling a product is called Average Revenue.
11.7 Mutual Determination of Elasticity of Demand, Average and
Marginal Revenue
If any firm knows any two factors from average revenue, marginal revenue and elasticity of demand,
then the third factor can be known by this equation—
AR
e = _________
d AR – MR
(Here e = Elasticity of demand; AR = Average Revenue; MR = Marginal Revenue)
d
In this elasticity of demand equation, the relations are defined by Fig. 11.10. This figure, shows that the
elasticity of demand at point P is—
PB
_____________
E = Lower Portion = ___
Upper Portion PQ
∆PMB is similar to triangle ∆QRP. So the average of its line is equal.
PB
____
___ = PM
QR
PQ
Cross a line from point P to OQ. Draw line QN from point P which intersects PR on its middle point S
and OX to point N. Actually, this line is MR curve.
In ∆PSA and ∆QRS
PS = SR ............... (Construction)
∠PSA = ∠QSR ............... (Vertically Opposite ∠S)
∠ QRS = ∠SPA ............... (Right ∠S)
230 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY