Page 387 - DECO503_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_AND_FINANCE_ENGLISH
P. 387
Unit 32 : India’s Balance of Payment
Notes
7. Overall
Balance 11,757 31,421 26,159 15,052 36,606 92,164 -20,080 -13441 13,050
8. F.E. Reserve Use
(Increase - /Decrease) As
percent of GDP-11,757 -31,421 -26,159 -15,052 -36,606 -92,164 20,080 +13441 13,050
Exports 9.4 11.0 12.2 13.0 13.84 13.5 15.6 14.4 15.9
Imports 11.8 13.3 17.1 19.4 20.05 21.0 25.4 23.1 24.2
Trade Balance -2.4 -2.3 -4.8 -6.4 -6.8 -7.4 -9.8 8.7 8.3
Invisible
Balance 3.1 4.6 4.5 5.2 5.7 6.2 7.4 7.0 5.5
Current Account
Balance 0.7 2.3 -0.4 -1.2 -1.1 -1.3 -2.4 -3.1 –2.8
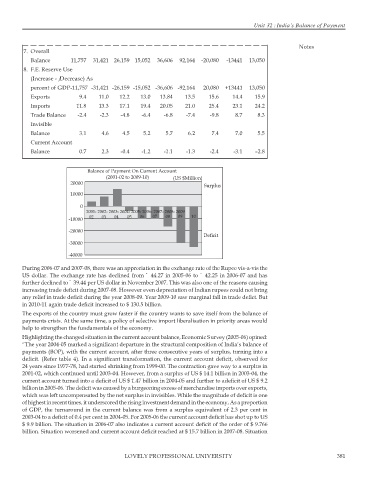
Balance of Payment On Current Account
(2001-02 to 2009-10) (US $Million)
20000
Surplus
10000
0
2001- 2002- 2003- 2004- 2005- 2006- 2007- 2008- 2009
02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10
-10000
-20000
Deficit
-30000
-40000
During 2006-07 and 2007-08, there was an appreciation in the exchange rate of the Rupee vis-a-vis the
US dollar. The exchange rate has declined from ` 44.27 in 2005-06 to ` 42.25 in 2006-07 and has
further declined to ` 39.44 per US dollar in November 2007. This was also one of the reasons causing
increasing trade deficit during 2007-08. However even depreciation of Indian rupees could not bring
any relief in trade deficit during the year 2008-09. Year 2009-10 saw marginal fall in trade defict. But
in 2010-11 again trade deficit increased to $ 130.5 billion.
The exports of the country must grow faster if the country wants to save itself from the balance of
payments crisis. At the same time, a policy of selective import liberalisation in priority areas would
help to strengthen the fundamentals of the economy.
Highlighting the changed situation in the current account balance, Economic Survey (2005-06) opined:
“The year 2004-05 marked a significant departure in the structural composition of India’s balance of
payments (BOP), with the current account, after three consecutive years of surplus, turning into a
deficit. (Refer table 4). In a significant transformation, the current account deficit, observed for
24 years since 1977-78, had started shrinking from 1999-00. The contraction gave way to a surplus in
2001-02, which continued until 2003-04. However, from a surplus of US $ 14.1 billion in 2003-04, the
current account turned into a deficit of US $ 1.47 billion in 2004-05 and further to adeficit of US $ 9.2
billion in 2005-06. The deficit was caused by a burgeoning excess of merchandise imports over exports,
which was left uncompensated by the net surplus in invisibles. While the magnitude of deficit is one
of highest in recent times, it underscored the rising investment demand in the economy, As a proportion
of GDP, the turnaround in the current balance was from a surplus equivalent of 2.3 per cent in
2003-04 to a deficit of 0.4 per cent in 2004-05. For 2005-06 the current account deficit has shot up to US
$ 9.9 billion. The situation in 2006-07 also indicates a current account deficit of the order of $ 9.766
billion. Situation worsened and current account deficit reached at $ 15.7 billion in 2007-08. Situation
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 381