Page 74 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 74
Statistical Methods in Economics
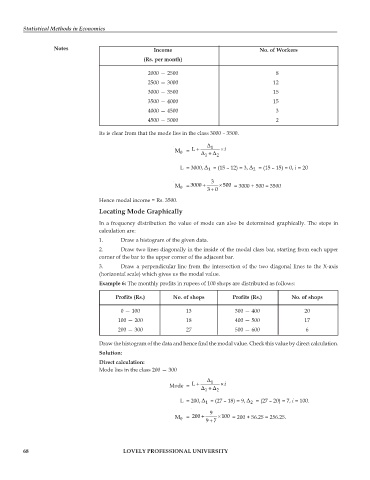
Notes Income No. of Workers
(Rs. per month)
2000 — 2500 8
2500 — 3000 12
3000 — 3500 15
3500 — 4000 15
4000 — 4500 3
4500 — 5000 2
Its is clear from that the mode lies in the class 3000 – 3500.
Δ 1
M 0 = L + Δ 1 + Δ 2 × i
L = 3000, Δ = (15 – 12) = 3, Δ = (15 – 15) = 0, i = 20
2
1
3
M 0 = 3000 + 30 × 500 = 3000 + 500 = 3500
+
Hence modal income = Rs. 3500.
Locating Mode Graphically
In a frequency distribution the value of mode can also be determined graphically. The steps in
calculation are:
1. Draw a histogram of the given data.
2. Draw two lines diagonally in the inside of the modal class bar, starting from each upper
corner of the bar to the upper corner of the adjacent bar.
3. Draw a perpendicular line from the intersection of the two diagonal lines to the X-axis
(horizontal scale) which gives us the modal value.
Example 6: The monthly profits in rupees of 100 shops are distributed as follows:
Profits (Rs.) No. of shops Profits (Rs.) No. of shops
0 — 100 13 300 — 400 20
100 — 200 18 400 — 500 17
200 — 300 27 500 — 600 6
Draw the histogram of the data and hence find the modal value. Check this value by direct calculation.
Solution:
Direct calculation:
Mode lies in the class 200 — 300
Δ 1
Mode = L + Δ 1 + Δ 2 × i
L = 200, Δ = (27 – 18) = 9, Δ = (27 – 20) = 7, i = 100.
2
1
9
M 0 = 200 + 97 × 100 = 200 + 56.25 = 256.25.
+
68 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY