Page 4 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_HINDI
P. 4
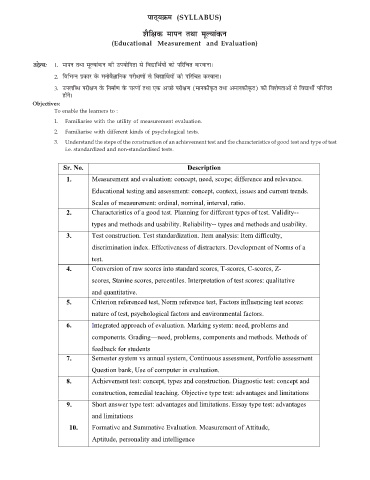
ikB~;Øe (SYLLABUS)
'kSf{kd ekiu rFkk ewY;kadu
(Educational Measurement and Evaluation)
mís';% 1- ekiu rFkk ewY;kadu dh mi;ksfxrk ls fo|kfFkZ;ksa dks ifjfpr djokukA
2- fofHkUu izdkj osQ euksoSKkfud ijh{k.kksa ls fo|kfFZk;ksa dks ifjfpr djokukA
3- miyfC/ ijh{k.k osQ fuekZ.k osQ pj.kksa rFkk ,d vPNs ijh{k.k (ekudhÑr rFkk vekudhÑr) dh fo'ks"krkvksa ls fo|kFkhZ ifjfpr
gksaxsA
Objectives:
To enable the learners to :
1. Familiarise with the utility of measurement evaluation.
2. Familiarise with different kinds of psychological tests.
3. Understand the steps of the construction of an achievement test and the characteristics of good test and type of test
i.e. standardized and non-standardised tests.
Sr. No. Description
1. Measurement and evaluation: concept, need, scope; difference and relevance.
Educational testing and assessment: concept, context, issues and current trends.
Scales of measurement: ordinal, nominal, interval, ratio.
2. Characteristics of a good test. Planning for different types of test. Validity--
types and methods and usability. Reliability-- types and methods and usability.
3. Test construction. Test standardization. Item analysis: Item difficulty,
discrimination index. Effectiveness of distracters. Development of Norms of a
test.
4. Conversion of raw scores into standard scores, T-scores, C-scores, Z-
scores, Stanine scores, percentiles. Interpretation of test scores: qualitative
and quantitative.
5. Criterion referenced test, Norm reference test, Factors influencing test scores:
nature of test, psychological factors and environmental factors.
6. Integrated approach of evaluation. Marking system: need, problems and
components. Grading—need, problems, components and methods. Methods of
feedback for students
7. Semester system vs annual system, Continuous assessment, Portfolio assessment
Question bank, Use of computer in evaluation.
8. Achievement test: concept, types and construction. Diagnostic test: concept and
construction, remedial teaching. Objective type test: advantages and limitations
9. Short answer type test: advantages and limitations. Essay type test: advantages
and limitations
10. Formative and Summative Evaluation. Measurement of Attitude,
Aptitude, personality and intelligence