Page 164 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 164
Unit 9: General Equilibrium of an Economy: IS-LM Analysis
There is an excess supply of money above the LM-curve, and hence we show ESM in regions Notes
I and II. Similarly, there is an excess demand of goods below IS-curve. Hence we show EDG for
II and III.
The directions of adjustments are represented by arrows.
Example: In IV there is excess demand for money, which causes interest rates to rise as
other assets (including stocks and bonds) are sold off for money and their prices decline. The
rising interest rates are shown by upward pointing arrows. There is also an excess supply of
goods in IV and hence, involuntary inventory accumulation, to which producing units (firms)
respond by reducing output.
Declining output is indicated by leftward pointing arrow. The adjustments shown by arrows
will ultimately lead, perhaps in a cyclical manner, to the point E, for example, starting from F,
we show the economy moving to E, with income and interest rate increasing along the adjustment
path indicated.
In short, income and interest rates adjust to the disequilibrium in both markets. Interest rates
fall when there is an excess supply of money and rise when there is an excess demand. Income
rises when aggregate demand for goods exceeds output, and falls when aggregate demand is
less than output. The system ultimately moves to the equilibrium point at E.
[Rate of interest tends to move vertically towards the LM-curve whereas level of income tends
to move horizontally toward the IS-curve. Arrows show direction of motion].
9.4.3 IS-LM Analysis
Monetary Policy in IS-LM Framework
Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply
of money, often targeting a rate of interest for the purpose of promoting economic growth and
stability. (You will study aspects of Monetary Policy in detail in Unit 13)
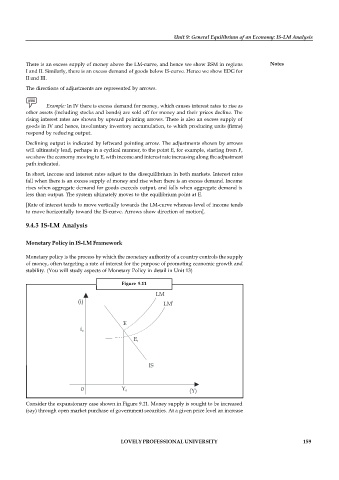
Figure 9.11
LM
(i)) 1
LM
E
i 0
E 1
IS
0 Y 0 (Y)
Consider the expansionary case shown in Figure 9.11. Money supply is sought to be increased
(say) through open market purchase of government securities. At a given price level an increase
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 159