Page 163 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 163
Macro Economics
Notes increases the demand for money. With a fixed supply of money, the interest rate has to rise to
ensure that the demand for money stays equal to the fixed supply. When the interest rate rises,
investment spending is reduced because investment is negatively related to rate of interest.
(dl/dr < 0)
Task Show with the help of a figure, the changes in general equilibrium when only the
interest rate changes.
9.4.2 Adjustment towards Equilibrium
Suppose our hypothetical economy were initially at a point like E in Figure 9.9 and that one of
the curves then shifted, so that the new equilibrium was at a point F. How would that new
equilibrium be reached? The adjustment would involve changes in both the interest rate and
level of income.
!
Caution Here we make two assumptions:
1. Since prices are assured to remain fixed, when demand increases, output increases
and vice versa (from Keynesian theory of income determination).
2. The interest rate rises when there is an excess demand for money and falls when
there is an excess supply of money (Keynesian liquidity preference theory).
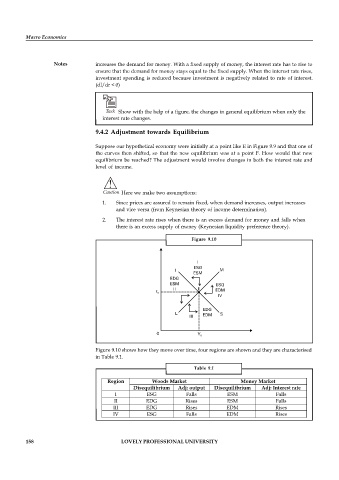
Figure 9.10
Figure 9.10 shows how they move over time, four regions are shown and they are characterised
in Table 9.1.
Table 9.1
Region Woods Market Money Market
Disequilibrium Adj: output Disequilibrium Adj: Interest rate
I ESG Falls ESM Falls
II EDG Rises ESM Falls
III EDG Rises EDM Rises
IV ESG Falls EDM Rises
158 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY