Page 160 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 160
Unit 9: General Equilibrium of an Economy: IS-LM Analysis
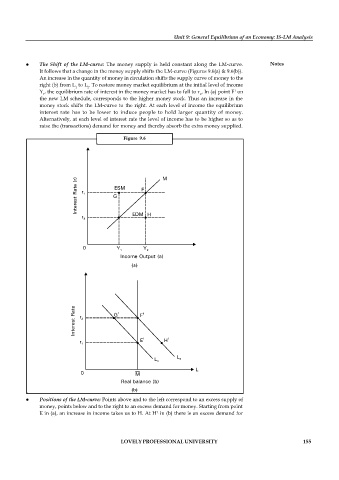
The Shift of the LM-curve: The money supply is held constant along the LM-curve. Notes
It follows that a change in the money supply shifts the LM-curve (Figures 9.6(a) & 9.6(b)).
An increase in the quantity of money in circulation shifts the supply curve of money to the
right (b) from L to L . To restore money market equilibrium at the initial level of income
1 2
1
Y , the equilibrium rate of interest in the money market has to fall to r . In (a) point F on
1 2
the new LM schedule, corresponds to the higher money stock. Thus an increase in the
money stock shifts the LM-curve to the right. At each level of income the equilibrium
interest rate has to be lower to induce people to hold larger quantity of money.
Alternatively, at each level of interest rate the level of income has to be higher so as to
raise the (transactions) demand for money and thereby absorb the extra money supplied.
Figure 9.6
(a)
(b)
Positions of the LM-curve: Points above and to the left correspond to an excess supply of
money, points below and to the right to an excess demand for money. Starting from point
1
E in (a), an increase in income takes us to H. At H in (b) there is an excess demand for
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 155