Page 165 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 165
Macro Economics
Notes in nominal supply of money also mean increase in real quantity of money. The LM schedule will
shift downward to the right as LM . The new equilibrium will be at point E with lower interest
1 1
rate and a higher level of income. The equilibrium income rises because the open market
purchase reduces the interest rate and thereby increase spending, particularly investment.
What is the process of adjustment to the monetary expansion? At the initial equilibrium point E,
the increase in money supply creates an excess supply of many to which the public responds, by
trying to buy the other assets. In the process, asset prices increase and yields decline. Because
money and asset markets adjust rapidly to change in money supply, in the Figure 9.11 equilibrium
shifts from points E to E where the money market clears and where the public is willing to hold
1
the larger real quantity of money because the interest rate has declined significantly. At point E
1
however, there is an excess demand for goods. The decline in the interest rates gives the initial
income Y , has raised aggregate demand and is causing inventories to run down. In response,
0
output expands and we start moving up along the LM schedule. The interest rate rises during the
adjustment process because the increase in output raises the demand for money, and the greater
demand for money needs to be checked by higher interest rates. At the new equilibrium point
E , the level of income is higher (Y ) and the interest rate is lower (i ).
1 1 1
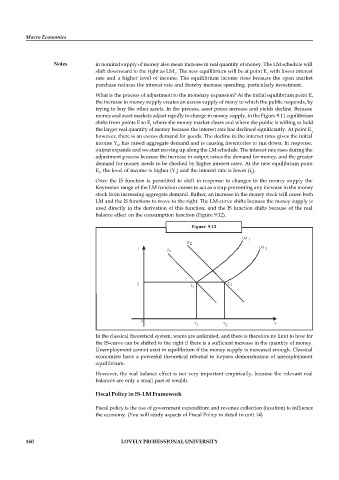
Once the IS function is permitted to shift in response to changes in the money supply the
Keynesian range of the LM function ceases to act as a trap preventing any increase in the money
stock from increasing aggregate demand. Rather, an increase in the money stock will cause both
LM and the IS functions to move to the right. The LM-curve shifts because the money supply is
used directly in the derivation of this function, and the IS function shifts because of the real
balance effect on the consumption function (Figure 9.12).
Figure 9.12
In the classical theoretical system, wants are unlimited, and there is therefore no limit to how far
the IS-curve can be shifted to the right if there is a sufficient increase in the quantity of money.
Unemployment cannot exist in equilibrium if the money supply is increased enough. Classical
economists have a powerful theoretical rebuttal to Keynes demonstration of unemployment
equilibrium.
However, the real balance effect is not very important empirically, because the relevant real
balances are only a small part of wealth.
Fiscal Policy in IS-LM Framework
Fiscal policy is the use of government expenditure and revenue collection (taxation) to influence
the economy. (You will study aspects of Fiscal Policy in detail in unit 14)
160 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY