Page 79 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 79
Cost Accounting – II
Notes (x) Then the graph indicates the break-even point, profit or loss at various level of output,
contribution, relationship between the marginal cost, fixed cost, total cost and margin of
safety.
Problem 8:
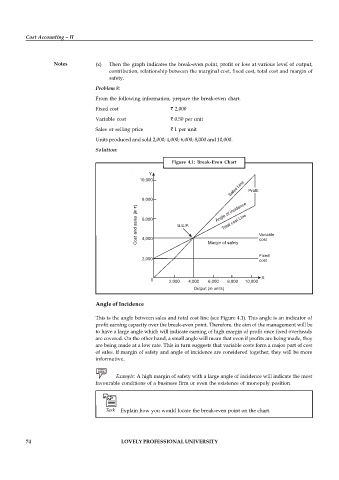
From the following information, prepare the break-even chart.
Fixed cost ` 2,000
Variable cost ` 0.50 per unit
Sales or selling price ` 1 per unit
Units produced and sold 2,000; 4,000; 6,000; 8,000 and 10,000.
Solution:
Figure 4.1: Break-Even Chart
Y
10,000
Sales Line Profit
8,000
Cost and sales (in `) Cost and sales (in Rs.) 6,000 B.E.P. Angle of incidence Variable
Total cost Line
4,000
cost
Margin of safety
Fixed
2,000
cost
X
0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000
Output (in units)
Angle of Incidence
This is the angle between sales and total cost line (see Figure 4.1). This angle is an indicator of
profit earning capacity over the break-even point. Therefore, the aim of the management will be
to have a large angle which will indicate earning of high margin of profit once fixed overheads
are covered. On the other hand, a small angle will mean that even if profits are being made, they
are being made at a low rate. This in turn suggests that variable costs form a major part of cost
of sales. If margin of safety and angle of incidence are considered together, they will be more
informative.
Example: A high margin of safety with a large angle of incidence will indicate the most
favourable conditions of a business firm or even the existence of monopoly position.
Task Explain how you would locate the break-even point on the chart.
74 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY