Page 84 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 84
Unit 4: Cost Volume Profit Analysis
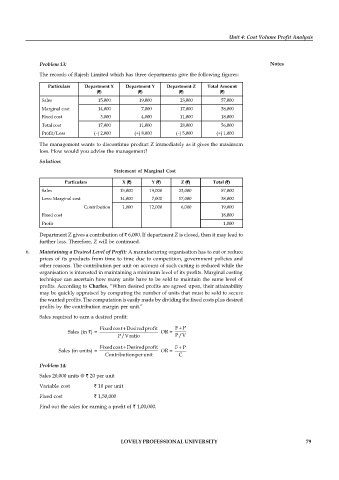
Problem 13: Notes
The records of Rajesh Limited which has three departments give the following figures:
Particulars Department X Department Y Department Z Total Amount
(`) (`) (`) (`)
Sales 15,000 19,000 23,000 57,000
Marginal cost 14,000 7,000 17,000 38,000
Fixed cost 3,000 4,000 11,000 18,000
Total cost 17,000 11,000 28,000 56,000
Profit/Loss (–) 2,000 (+) 8,000 (–) 5,000 (+) 1,000
The management wants to discontinue product Z immediately as it gives the maximum
loss. How would you advise the management?
Solution:
Statement of Marginal Cost
Particulars X (`) Y (`) Z (`) Total (`)
Sales 15,000 19,000 23,000 57,000
Less: Marginal cost 14,000 7,000 17,000 38,000
Contribution 1,000 12,000 6,000 19,000
Fixed cost 18,000
Profit 1,000
Department Z gives a contribution of ` 6,000. If department Z is closed, then it may lead to
further loss. Therefore, Z will be continued.
6. Maintaining a Desired Level of Profit: A manufacturing organisation has to cut or reduce
prices of its products from time to time due to competition, government policies and
other reasons. The contribution per unit on account of such cutting is reduced while the
organisation is interested in maintaining a minimum level of its profits. Marginal costing
technique can ascertain how many units have to be sold to maintain the same level of
profits. According to Charles, “When desired profits are agreed upon, their attainability
may be quickly appraised by computing the number of units that must be sold to secure
the wanted profits. The computation is easily made by dividing the fixed costs plus desired
profits by the contribution margin per unit.”
Sales required to earn a desired profit:
Fixedcost Desiredprofit F P
Sales (in `) = OR =
P/Vratio P/V
Fixedcost Desiredprofit F P
Sales (in units) = OR =
Contributionperunit C
Problem 14:
Sales 20,000 units @ ` 20 per unit
Variable cost ` 10 per unit
Fixed cost ` 1,50,000
Find out the sales for earning a profit of ` 1,00,000.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 79