Page 87 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 87
Cost Accounting – II
Notes
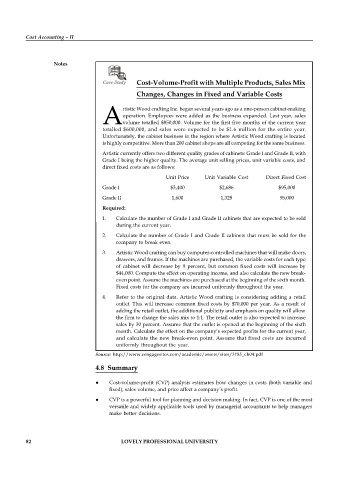
Case Study Cost-Volume-Profit with Multiple Products, Sales Mix
Changes, Changes in Fixed and Variable Costs
rtistic Wood crafting Inc. began several years ago as a one-person cabinet-making
operation. Employees were added as the business expanded. Last year, sales
Avolume totalled $850,000. Volume for the first five months of the current year
totalled $600,000, and sales were expected to be $1.6 million for the entire year.
Unfortunately, the cabinet business in the region where Artistic Wood crafting is located
is highly competitive. More than 200 cabinet shops are all competing for the same business.
Artistic currently offers two different quality grades of cabinets: Grade I and Grade II, with
Grade I being the higher quality. The average unit selling prices, unit variable costs, and
direct fixed costs are as follows:
Unit Price Unit Variable Cost Direct Fixed Cost
Grade I $3,400 $2,686 $95,000
Grade II 1,600 1,328 95,000
Required:
1. Calculate the number of Grade I and Grade II cabinets that are expected to be sold
during the current year.
2. Calculate the number of Grade I and Grade II cabinets that must be sold for the
company to break even.
3. Artistic Wood crafting can buy computer-controlled machines that will make doors,
drawers, and frames. If the machines are purchased, the variable costs for each type
of cabinet will decrease by 9 percent, but common fixed costs will increase by
$44,000. Compute the effect on operating income, and also calculate the new break-
even point. Assume the machines are purchased at the beginning of the sixth month.
Fixed costs for the company are incurred uniformly throughout the year.
4. Refer to the original data. Artistic Wood crafting is considering adding a retail
outlet. This will increase common fixed costs by $70,000 per year. As a result of
adding the retail outlet, the additional publicity and emphasis on quality will allow
the firm to change the sales mix to 1:1. The retail outlet is also expected to increase
sales by 30 percent. Assume that the outlet is opened at the beginning of the sixth
month. Calculate the effect on the company’s expected profits for the current year,
and calculate the new break-even point. Assume that fixed costs are incurred
uniformly throughout the year.
Source: http://www.cengagesites.com/academic/assets/sites/3185_ch04.pdf
4.8 Summary
Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis estimates how changes in costs (both variable and
fixed), sales volume, and price affect a company’s profit.
CVP is a powerful tool for planning and decision making. In fact, CVP is one of the most
versatile and widely applicable tools used by managerial accountants to help managers
make better decisions.
82 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY