Page 102 - DCOM208_BANKING_THEORY_AND_PRACTICE
P. 102
Unit 7: Loans and Advances
Describe loan procedure followed by banks Notes
Evaluate consumer and commercial loans
Introduction
In the previous unit, we dealt with the various types of deposit accounts including no-frills
accounts. This unit will helps you to understand the various aspects related to loans and advances.
The various section and sub section of this unit will also summarize the concept of evaluating
consumer and commercial loans. Efficient management of Loans and Advances portfolio has
assumed greater significance as it is the largest asset of the bank having direct impact on its
profitability. In the wake of the continued tightening of norms of income recognition, asset
classification and provisioning, increased competition and emergence of new types of risks in
the financial sector, it has become imperative that the credit functions are strengthened. RBI has
also been emphasizing banks to evolve suitable guidelines for effective management and control
of credit risks.
7.1 Types of Loans
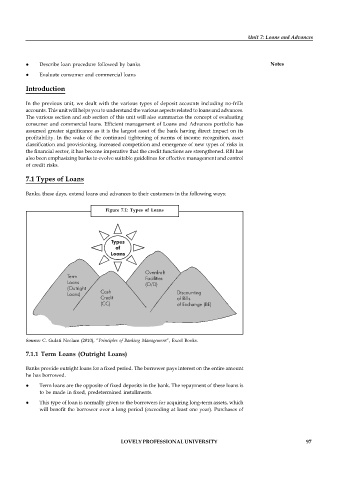
Banks, these days, extend loans and advances to their customers in the following ways:
Figure 7.1: Types of Loans
Types
of
Loans
Overdraft
Term Facilities
Loans (O/D)
(Outright
Loans) Cash Discounting
Credit of Bills
(CC) of Exchange (BE)
Source: C. Gulati Neelam (2010), ”Principles of Banking Management”, Excel Books.
7.1.1 Term Loans (Outright Loans)
Banks provide outright loans for a fixed period. The borrower pays interest on the entire amount
he has borrowed.
Term loans are the opposite of fixed deposits in the bank. The repayment of these loans is
to be made in fixed, predetermined installments.
This type of loan is normally given to the borrowers for acquiring long-term assets, which
will benefit the borrower over a long period (exceeding at least one year). Purchases of
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 97