Page 217 - DMGT209_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_II
P. 217
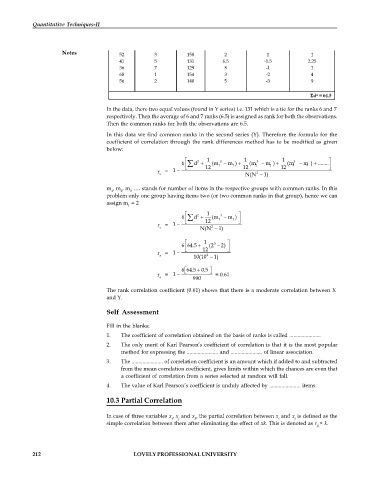
X Ranks of X Y Ranks of Y Difference Squared
(R1 ) (R2) (R1 – R2) (d) difference ( d )
2
24 9 110 10 -1 1
Quantitative Techniques-II
29 8 126 9 -1 1
23 10 145 4 6 36
38 6 131 6.5 -0.5 0.25
46 4 163 1 3 9
Notes 52 3 158 2 1 1
41 5 131 6.5 -1.5 2.25
36 7 129 8 -1 1
68 1 154 3 -2 4
56 2 140 5 -3 9
2
d = 64.5
In the data, there two equal values (found in Y series) i.e. 131 which is a tie for the ranks 6 and 7
respectively. Then the average of 6 and 7 ranks (6.5) is assigned as rank for both the observations.
Then the common ranks for both the observations are 6.5.
In this data we find common ranks in the second series (Y). Therefore the formula for the
coefficient of correlation through the rank differences method has to be modified as given
below:
2 1 3 1 3 1 3
6 d (m m ) (m 2 m ) (m m ) ........
1
2
3
1
3
r = 1 12 12 2 12
s N(N 1)
m , m , m …. stands for number of items in the respective groups with common ranks. In this
1 2 3
problem only one group having items two (or two common ranks in that group), hence we can
assign m = 2
1
2 1 3
6 d (m m )
12 1 1
r = 1
2
s N(N 1)
1 3
6 64.5 (2 2)
12
r = 1
s 10(10 1)
2
6 64.5 0.5
r = 1 = 0.61
s 990
The rank correlation coefficient (0.61) shows that there is a moderate correlation between X
and Y.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. The coefficient of correlation obtained on the basis of ranks is called .......................
2. The only merit of Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation is that it is the most popular
method for expressing the ....................... and ....................... of linear association.
3. The ....................... of correlation coefficient is an amount which if added to and subtracted
from the mean correlation coefficient, gives limits within which the chances are even that
a coefficient of correlation from a series selected at random will fall.
4. The value of Karl Pearson’s coefficient is unduly affected by ....................... items.
10.3 Partial Correlation
In case of three variables x , x and x , the partial correlation between x and x is defined as the
i j k i j
simple correlation between them after eliminating the effect of xk. This is denoted as r × k.
ij
212 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY