Page 128 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 128
Unit 8: Cost Analysis
Thus, average fixed cost is the fixed cost per unit of output. Since total fixed cost is a constant Notes
quantity, average fixed cost will steadily fall as output increases. Therefore, average fixed cost
curve slopes downward throughout its length. As output increases, the total fixed cost spreads
over more and more units and, therefore, average fixed cost becomes less and less.
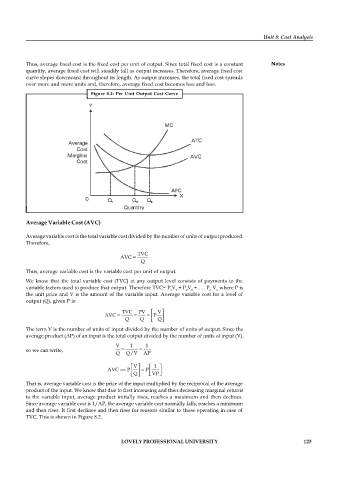
Figure 8.2: Per Unit Output Cost Curve
Average Variable Cost (AVC)
Average variable cost is the total variable cost divided by the number of units of output produced.
Therefore,
TVC
AVC
Q
Thus, average variable cost is the variable cost per unit of output.
We know that the total variable cost (TVC) at any output level consists of payments to the
variable factors used to produce that output. Therefore TVC= P V + P V + …. P V where P is
1 1 2 2 n n
the unit price and V is the amount of the variable input. Average variable cost for a level of
output (Q), given P is:
TVC PV V
AVC P
Q Q Q
The term V is the number of units of input divided by the number of units of output. Since the
average product (AP) of an input is the total output divided by the number of units of input (V),
V 1 1
so we can write,
Q Q/V AP
V 1
AVC P P
Q VP
That is, average variable cost is the price of the input multiplied by the reciprocal of the average
product of the input. We know that due to first increasing and then decreasing marginal returns
to the variable input, average product initially rises, reaches a maximum and then declines.
Since average variable cost is 1/AP, the average variable cost normally falls, reaches a minimum
and then rises. It first declines and then rises for reasons similar to those operating in case of
TVC. This is shown in Figure 8.2.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 123