Page 77 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 77
Managerial Economics
Notes The measurement of elasticity is done by two methods, namely, Geometrical Method and
Arithmetical Method.
A geometrical way of measuring the elasticity at any point on a demand curve is now in order.
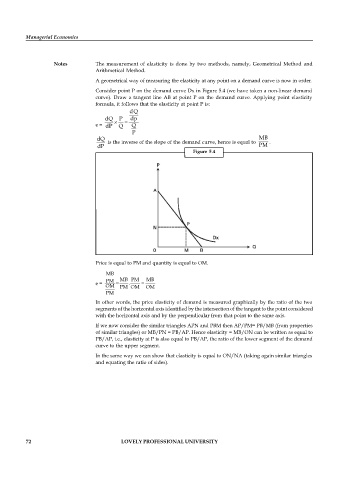
Consider point P on the demand curve Dx in Figure 5.4 (we have taken a non-linear demand
curve). Draw a tangent line AB at point P on the demand curve. Applying point elasticity
formula, it follows that the elasticity at point P is:
dQ
dQ P dp
e = dP Q Q
P
dQ MB
is the inverse of the slope of the demand curve, hence is equal to .
dP PM
Figure 5.4
Price is equal to PM and quantity is equal to OM.
MB
PM MB PM MB
e = .
OM PM OM OM
PM
In other words, the price elasticity of demand is measured graphically by the ratio of the two
segments of the horizontal axis identified by the intersection of the tangent to the point considered
with the horizontal axis and by the perpendicular from that point to the same axis.
If we now consider the similar triangles APN and PBM then AP/PM= PB/MB (from properties
of similar triangles) or MB/PN = PB/AP. Hence elasticity = MB/ON can be written as equal to
PB/AP, i.e., elasticity at P is also equal to PB/AP, the ratio of the lower segment of the demand
curve to the upper segment.
In the same way we can show that elasticity is equal to ON/NA (taking again similar triangles
and equating the ratio of sides).
72 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY