Page 222 - DMGT405_FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT
P. 222
Financial Management
Notes
!
Caution The amount of overheads may be separately calculated for different types of
overheads. In the case of settling overheads, the relevant claim should be sales volume
instead of production volume.
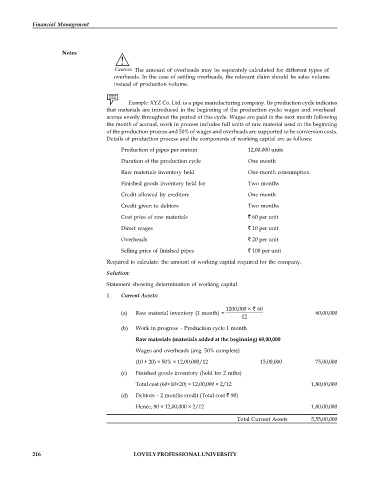
Example: XYZ Co. Ltd. is a pipe manufacturing company. Its production cycle indicates
that materials are introduced in the beginning of the production cycle; wages and overhead
accrue evenly throughout the period of this cycle. Wages are paid in the next month following
the month of accrual, work in process includes full units of raw material used in the beginning
of the production process and 50% of wages and overheads are supported to be conversion costs.
Details of production process and the components of working capital are as follows:
Production of pipes per annum 12,00,000 units
Duration of the production cycle One month
Raw materials inventory held One-month consumption
Finished goods inventory held for Two months
Credit allowed by creditors One month
Credit given to debtors Two months
Cost price of raw materials 60 per unit
Direct wages 10 per unit
Overheads 20 per unit
Selling price of finished pipes 100 per unit
Required to calculate: the amount of working capital required for the company.
Solution:
Statement showing determination of working capital
1. Current Assets:
1200,000 × 60
(a) Raw material inventory (1 month) = 60,00,000
12
(b) Work in progress – Production cycle 1 month
Raw materials (materials added at the beginning) 60,00,000
Wages and overheads (avg. 50% complete)
(10 + 20) × 50% × 12,00,000/12 15,00,000 75,00,000
(c) Finished goods inventory (hold for 2 mths)
Total cost (60+10+20) × 12,00,000 × 2/12 1,80,00,000
(d) Debtors – 2 months credit (Total cost 90)
Hence, 90 × 12,00,000 × 2/12 1,80,00,000
Total Current Assets 5,55,00,000
216 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY