Page 43 - DCOM409_CONTEMPORARY_ACCOUNTING
P. 43
Contemporary Accounting
Notes business. This should be done by eliminating the effects of change in price levels in the amounts
of receivables and payables. The amounts of receivables and payables have been compared for
this purpose by adjusting their figures on the basis of average price indices as shown below:
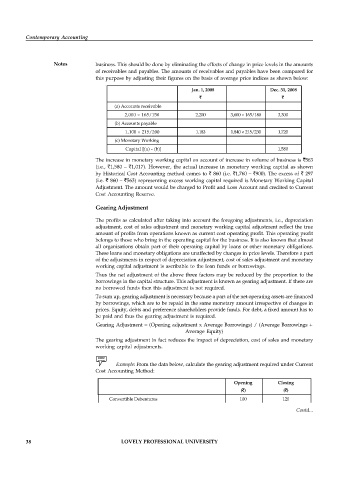
Jan. 1, 2008 Dec. 31, 2008
` `
(a) Accounts receivable
2,000 × 165/150 2,200 3,600 × 165/180 3,300
(b) Accounts payable
1,100 × 215/200 1,183 1,840 × 215/230 1,720
(c) Monetary Working
Capital [(a) - (b)] 1,580
The increase in monetary working capital on account of increase in volume of business is `563
(i.e., `1,580 – `1,017). However, the actual increase in monetary working capital as shown
by Historical Cost Accounting method comes to ` 860 (i.e. `1,760 – `900). The excess of ` 297
(i.e. ` 860 – `563) representing excess working capital required is Monetary Working Capital
Adjustment. The amount would be charged to Profit and Loss Account and credited to Current
Cost Accounting Reserve.
Gearing Adjustment
The profits as calculated after taking into account the foregoing adjustments, i.e., depreciation
adjustment, cost of sales adjustment and monetary working capital adjustment reflect the true
amount of profits from operations known as current cost operating profit. This operating profit
belongs to those who bring in the operating capital for the business. It is also known that almost
all organisations obtain part of their operating capital by loans or other monetary obligations.
These loans and monetary obligations are unaffected by changes in price levels. Therefore a part
of the adjustments in respect of depreciation adjustment, cost of sales adjustment and monetary
working capital adjustment is ascribable to the loan funds or borrowings.
Thus the net adjustment of the above three factors may be reduced by the proportion to the
borrowings in the capital structure. This adjustment is known as gearing adjustment. If there are
no borrowed funds then this adjustment is not required.
To sum up, gearing adjustment is necessary because a part of the net operating assets are financed
by borrowings, which are to be repaid in the same monetary amount irrespective of changes in
prices. Equity, debts and preference shareholders provide funds. For debt, a fixed amount has to
be paid and thus the gearing adjustment is required.
Gearing Adjustment = (Opening adjustment x Average Borrowings) / (Average Borrowings +
Average Equity)
The gearing adjustment in fact reduces the impact of depreciation, cost of sales and monetary
working capital adjustments.
Example: From the data below, calculate the gearing adjustment required under Current
Cost Accounting Method:
Opening Closing
(`) (`)
Convertible Debentures 100 120
Contd...
38 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY