Page 297 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 297
Security Analysis and Portfolio Management
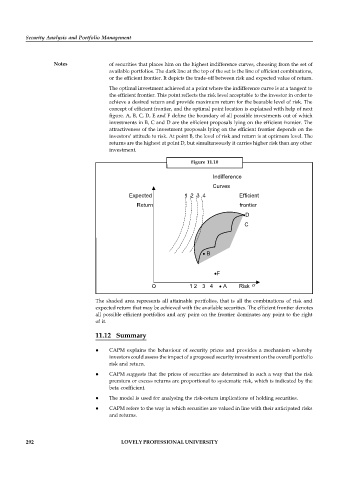
Notes of securities that places him on the highest indifference curves, choosing from the set of
available portfolios. The dark line at the top of the set is the line of efficient combinations,
or the efficient frontier. It depicts the trade-off between risk and expected value of return.
The optimal investment achieved at a point where the indifference curve is at a tangent to
the efficient frontier. This point reflects the risk level acceptable to the investor in order to
achieve a desired return and provide maximum return for the bearable level of risk. The
concept of efficient frontier, and the optimal point location is explained with help of next
figure. A, B, C, D, E and F define the boundary of all possible investments out of which
investments in B, C and D are the efficient proposals lying on the efficient frontier. The
attractiveness of the investment proposals lying on the efficient frontier depends on the
investors’ attitude to risk. At point B, the level of risk and return is at optimum level. The
returns are the highest at point D, but simultaneously it carries higher risk than any other
investment.
Figure 11.10
Indifference
Curves
Expected 1 2 3 4 Efficient
Return frontier
D
C
E
B
F
O 1 2 3 4 A Risk
The shaded area represents all attainable portfolios, that is all the combinations of risk and
expected return that may be achieved with the available securities. The efficient frontier denotes
all possible efficient portfolios and any point on the frontier dominates any point to the right
of it.
11.12 Summary
CAPM explains the behaviour of security prices and provides a mechanism whereby
investors could assess the impact of a proposed security investment on the overall portfolio
risk and return.
CAPM suggests that the prices of securities are determined in such a way that the risk
premium or excess returns are proportional to systematic risk, which is indicated by the
beta coefficient.
The model is used for analysing the risk-return implications of holding securities.
CAPM refers to the way in which securities are valued in line with their anticipated risks
and returns.
292 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY