Page 155 - DCOM505_WORKING_CAPITAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 155
Working Capital Management
Notes
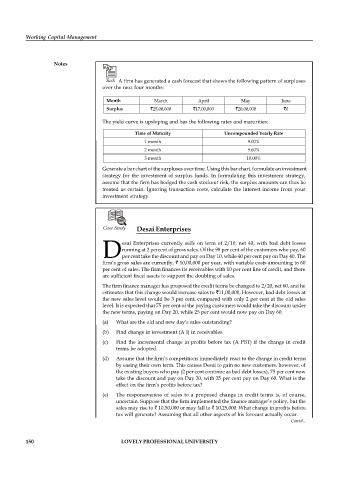
Task A firm has generated a cash forecast that shows the following pattern of surpluses
over the next four months:
Month March April May June
Surplus `25,00,000 `17,00,000 `20,00,000 `0
The yield curve is upsloping and has the following rates and maturities:
Time of Maturity Uncompounded Yearly Rate
1 month 9.00%
2 month 9.60%
3 month 10.00%
Generate a bar chart of the surpluses over time. Using this bar chart, formulate an investment
strategy for the investment of surplus funds. In formulating this investment strategy,
assume that the firm has hedged the cash stockout risk; the surplus amounts can thus be
treated as certain. Ignoring transaction costs, calculate the interest income from your
investment strategy.
Case Study Desai Enterprises
esai Enterprises currently sells on term of 2/10, net 40, with bad debt losses
running at 2 percent of gross sales. Of the 98 per cent of the customers who pay, 60
Dper cent take the discount and pay on Day 10, while 40 per cent pay on Day 40. The
firm’s gross sales are currently, ` 10,00,000 per year, with variable costs amounting to 60
per cent of sales. The firm finances its receivables with 10 per cent line of credit, and there
are sufficient fixed assets to support the doubling of sales.
The firm finance manager has proposed the credit terms be changed to 2/20, net 60, and he
estimates that this change would increase sales to `11,00,000, However, bad debt losses at
the new sales level would be 3 per cent, compared with only 2 per cent at the old sales
level. It is expected that 75 per cent of the paying customers would take the discount under
the new terms, paying on Day 20, while 25 per cent would now pay on Day 60.
(a) What are the old and new day’s sales outstanding?
(b) Find change in investment (A I) in receivables.
(c) Find the incremental change in profits before tax (A PBT) if the change in credit
terms be adopted.
(d) Assume that the firm’s competitions immediately react to the change in credit terms
by easing their own term. This causes Desai to gain no new customers, however, of
the existing buyers who pay (2 per cent continue as bad debt losses), 75 per cent now
take the discount and pay on Day 20, with 25 per cent pay on Day 60. What is the
effect on the firm’s profits before tax?
(e) The responsiveness of sales to a proposed change in credit terms is, of course,
uncertain. Suppose that the firm implemented the finance manager’s policy, but the
sales may rise to ` 10,50,000 or may fall to ` 10,25,000. What change in profits before
tax will generate? Assuming that all other aspects of his forecast actually occur.
Contd...
150 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY