Page 174 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 174
Unit 10: Clocked Sequential Circuits
The K-maps of SA and RA is shown in the Figure 10.7. Other K-maps can be obtained similarly Notes
and the equations derived are shown in the Figure 10.9.
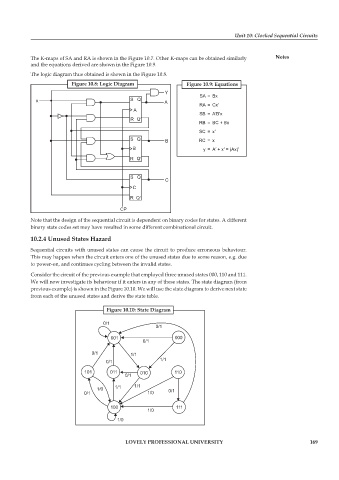
The logic diagram thus obtained is shown in the Figure 10.8.
Figure 10.8: Logic Diagram Figure 10.9: Equations
SA = Bx
RA = Cx′
SB = A′B′x
RB = BC + Bx
SC = x′
RC = x
y = A′ + x′ = (Ax)′
Note that the design of the sequential circuit is dependent on binary codes for states. A different
binary state codes set may have resulted in some different combinational circuit.
10.2.4 Unused States Hazard
Sequential circuits with unused states can cause the circuit to produce erroneous behaviour.
This may happen when the circuit enters one of the unused states due to some reason, e.g. due
to power-on, and continues cycling between the invalid states.
Consider the circuit of the previous example that employed three unused states 000, 110 and 111.
We will now investigate its behaviour if it enters in any of these states. The state diagram (from
previous example) is shown in the Figure 10.10. We will use the state diagram to derive next state
from each of the unused states and derive the state table.
Figure 10.10: State Diagram
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 169