Page 35 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 35
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes
other logic gates. If you need to connect its output to more logic gates, you can use a buffer to
increase the number of logic gates you can connect this output to.
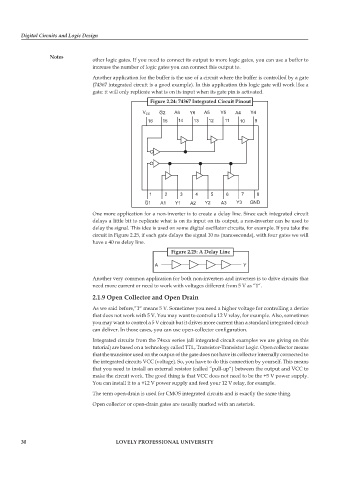
Another application for the buffer is the use of a circuit where the buffer is controlled by a gate
(74367 integrated circuit is a good example). In this application this logic gate will work like a
gate: it will only replicate what is on its input when its gate pin is activated.
Figure 2.24: 74367 Integrated Circuit Pinout
V G2 A6 Y6 A5 Y5 A4 Y4
CC
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
G1 A1 Y1 A2 Y2 A3 Y3 GND
One more application for a non-inverter is to create a delay line. Since each integrated circuit
delays a little bit to replicate what is on its input on its output, a non-inverter can be used to
delay the signal. This idea is used on some digital oscillator circuits, for example. If you take the
circuit in Figure 2.25, if each gate delays the signal 10 ns (nanoseconds), with four gates we will
have a 40 ns delay line.
Figure 2.25: A Delay Line
Another very common application for both non-inverters and inverters is to drive circuits that
need more current or need to work with voltages different from 5 V as ”1“.
2.1.9 Open Collector and Open Drain
As we said before,”1“ means 5 V. Sometimes you need a higher voltage for controlling a device
that does not work with 5 V. You may want to control a 12 V relay, for example. Also, sometimes
you may want to control a 5 V circuit but it drives more current than a standard integrated circuit
can deliver. In those cases, you can use open-collector configuration.
Integrated circuits from the 74xxx series (all integrated circuit examples we are giving on this
tutorial) are based on a technology called TTL, Transistor-Transistor Logic. Open collector means
that the transistor used on the output of the gate does not have its collector internally connected to
the integrated circuits VCC (voltage). So, you have to do this connection by yourself. This means
that you need to install an external resistor (called ”pull-up“) between the output and VCC to
make the circuit work. The good thing is that VCC does not need to be the +5 V power supply.
You can install it to a +12 V power supply and feed your 12 V relay, for example.
The term open-drain is used for CMOS integrated circuits and is exactly the same thing.
Open collector or open-drain gates are usually marked with an asterisk.
30 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY