Page 34 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 34
Unit 2: Logic Gates
So its output will only be at ”1“ when all its inputs have the same value. Otherwise its output Notes
will be ”0“.
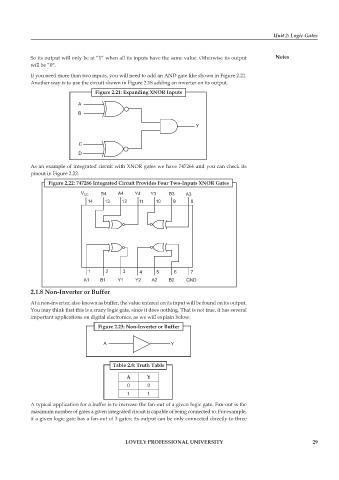
If you need more than two inputs, you will need to add an AND gate like shown in Figure 2.21.
Another way is to use the circuit shown in Figure 2.18 adding an inverter on its output.
Figure 2.21: Expanding XNOR Inputs
As an example of integrated circuit with XNOR gates we have 747266 and you can check its
pinout in Figure 2.22.
Figure 2.22: 747266 Integrated Circuit Provides Four Two-Inputs XNOR Gates
2.1.8 Non-Inverter or Buffer
At a non-inverter, also known as buffer, the value entered on its input will be found on its output.
You may think that this is a crazy logic gate, since it does nothing. That is not true, it has several
important applications on digital electronics, as we will explain below:
Figure 2.23: Non-Inverter or Buffer
Table 2.8: Truth Table
A Y
0 0
1 1
A typical application for a buffer is to increase the fan-out of a given logic gate. Fan-out is the
maximum number of gates a given integrated circuit is capable of being connected to. For example,
if a given logic gate has a fan-out of 3 gates; its output can be only connected directly to three
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 29