Page 38 - DCAP310_INTRODUCTION_TO_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE_AND_EXPERT_SYSTEMS
P. 38
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence & Expert Systems
Notes representation can best be understood in terms of five distinct roles it plays, each crucial to the
task at hand:
KR is most fundamentally a surrogate, a substitute for the thing itself, used to enable an
entity to determine consequences by thinking rather than acting, i.e., by reasoning about
the world rather than taking action in it.
It is a set of ontological commitments, i.e., an answer to the question: In what terms should
I think about the world?
It is a fragmentary theory of intelligent reasoning, expressed in terms of three components:
(i) the representation’s fundamental conception of intelligent reasoning; (ii) the set of
inferences the representation sanctions; and (iii) the set of inferences it recommends.
It is a medium for pragmatically efficient computation, i.e., the computational environment
in which thinking is accomplished. One contribution to this pragmatic efficiency is supplied
by the guidance a representation provides for organizing information so as to facilitate
making the recommended inferences.
It is a medium of human expression, i.e., a language in which we say things about the
world.”
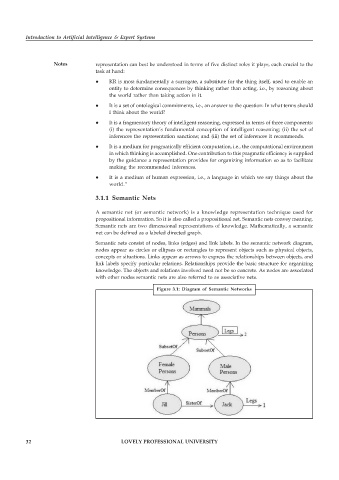
3.1.1 Semantic Nets
A semantic net (or semantic network) is a knowledge representation technique used for
propositional information. So it is also called a propositional net. Semantic nets convey meaning.
Semantic nets are two dimensional representations of knowledge. Mathematically, a semantic
net can be defined as a labeled directed graph.
Semantic nets consist of nodes, links (edges) and link labels. In the semantic network diagram,
nodes appear as circles or ellipses or rectangles to represent objects such as physical objects,
concepts or situations. Links appear as arrows to express the relationships between objects, and
link labels specify particular relations. Relationships provide the basic structure for organizing
knowledge. The objects and relations involved need not be so concrete. As nodes are associated
with other nodes semantic nets are also referred to as associative nets.
Figure 3.1: Diagram of Semantic Networks
32 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY