Page 169 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 169
Principles of Operating Systems
Notes
a 32-bit machine with page size of 512 bytes. The logical-address space of a process is divided
into four equal sections, each of which consists of 230 bytes.
Each section represents a different part of the logical-address space of a process. The first 2 high-
order bits of the logical address designate the appropriate section. The next 21 bits represent the
logical page number of that section, and the final 9 bits represent an offset in the desired page.
By partitioning the page table in this manner, the operating system can leave partitions unused
until a process needs them. An address on the VAX architecture is as follows:
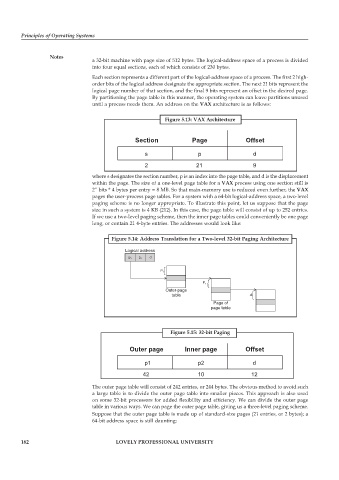
Figure 5.13: VAX Architecture
Section Page Offset
s p d
2 21 9
where s designates the section number, p is an index into the page table, and d is the displacement
within the page. The size of a one-level page table for a VAX process using one section still is
2” bits * 4 bytes per entry = 8 MB. So that main-memory use is reduced even further, the VAX
pages the user-process page tables. For a system with a 64-bit logical-address space, a two-level
paging scheme is no longer appropriate. To illustrate this point, let us suppose that the page
size in such a system is 4 KB (212). In this case, the page table will consist of up to 252 entries.
If we use a two-level paging scheme, then the inner page tables could conveniently be one page
long, or contain 21 4-byte entries. The addresses would look like:
Figure 5.14: Address Translation for a Two-level 32-bit Paging Architecture
Logical address
d
p 1 p 2
P 1
P 2
Outer-page
table d
Page of
page table
Figure 5.15: 32-bit Paging
Outer page Inner page Offset
p1 p2 d
42 10 12
The outer page table will consist of 242 entries, or 244 bytes. The obvious method to avoid such
a large table is to divide the outer page table into smaller pieces. This approach is also used
on some 32-bit processors for added flexibility and efficiency. We can divide the outer page
table in various ways. We can page the outer page table, giving us a three-level paging scheme.
Suppose that the outer page table is made up of standard-size pages (21 entries, or 2 bytes); a
64-bit address space is still daunting:
162 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY