Page 206 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 206
Unit 13: Advanced Computer Graphics
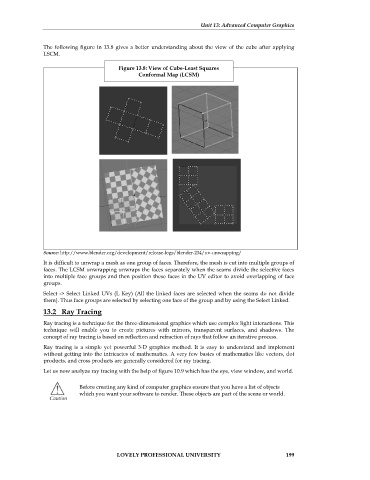
The following figure in 13.8 gives a better understanding about the view of the cube after applying
LSCM.
Figure 13.8: View of Cube-Least Squares
Conformal Map (LCSM)
Source: http://www.blender.org/development/release-logs/blender-234/uv-unwrapping/
It is difficult to unwrap a mesh as one group of faces. Therefore, the mesh is cut into multiple groups of
faces. The LCSM unwrapping unwraps the faces separately when the seams divide the selective faces
into multiple face groups and then position these faces in the UV editor to avoid overlapping of face
groups.
Select -> Select Linked UVs (L Key) (All the linked faces are selected when the seams do not divide
them). Thus face groups are selected by selecting one face of the group and by using the Select Linked.
13.2 Ray Tracing
Ray tracing is a technique for the three-dimensional graphics which use complex light interactions. This
technique will enable you to create pictures with mirrors, transparent surfaces, and shadows. The
concept of ray tracing is based on reflection and refraction of rays that follow an iterative process.
Ray tracing is a simple yet powerful 3-D graphics method. It is easy to understand and implement
without getting into the intricacies of mathematics. A very few basics of mathematics like vectors, dot
products, and cross products are generally considered for ray tracing.
Let us now analyze ray tracing with the help of figure 10.9 which has the eye, view window, and world.
Before creating any kind of computer graphics ensure that you have a list of objects
which you want your software to render. These objects are part of the scene or world.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 199