Page 18 - DCAP602_NETWORK_OPERATING_SYSTEMS_I
P. 18
Network Operating Systems-I
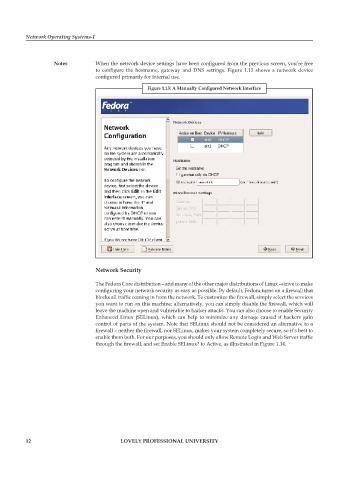
notes When the network device settings have been configured from the previous screen, you’re free
to configure the hostname, gateway and DNS settings. Figure 1.13 shows a network device
configured primarily for internal use.
Figure 1.13: A Manually Configured Network Interface
network security
The Fedora Core distribution – and many of the other major distributions of Linux –strive to make
configuring your network security as easy as possible. By default, Fedora turns on a firewall that
blocks all traffic coming in from the network. To customize the firewall, simply select the services
you want to run on this machine; alternatively, you can simply disable the firewall, which will
leave the machine open and vulnerable to hacker attacks. You can also choose to enable Security
Enhanced Linux (SELinux), which can help to minimize any damage caused if hackers gain
control of parts of the system. Note that SELinux should not be considered an alternative to a
firewall – neither the firewall, nor SELinux, makes your system completely secure, so it’s best to
enable them both. For our purposes, you should only allow Remote Login and Web Server traffic
through the firewall, and set Enable SELinux? to Active, as illustrated in Figure 1.14.
12 LoveLy professionaL university