Page 223 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 223
Operating System
Notes Access Control is also an entirely different security concept. Access control refers to general
rules allowing hosts, users or applications access to specific parts of a network. Typically, access
control helps organizations segment networks and limit access.
While an IPS has the ability to block access to users, hosts or applications, it does so only when
malicious code has been discovered. As such, IPS does not necessarily serve as an access control
device. While it has some access control abilities, firewalls and network access control (NAC)
technologies are better suited to provide these features.
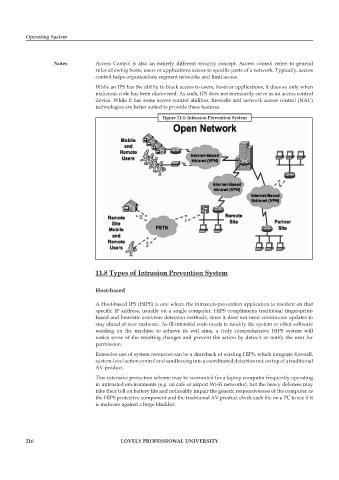
Figure 11.4: Intrusion Prevention System
11.8 Types of Intrusion Prevention System
Host-based
A Host-based IPS (HIPS) is one where the intrusion-prevention application is resident on that
specific IP address, usually on a single computer. HIPS compliments traditional fi nger-print-
based and heuristic antivirus detection methods, since it does not need continuous updates to
stay ahead of new malware. As ill-intended code needs to modify the system or other software
residing on the machine to achieve its evil aims, a truly comprehensive HIPS system will
notice some of the resulting changes and prevent the action by default or notify the user for
permission.
Extensive use of system resources can be a drawback of existing HIPS, which integrate fi rewall,
system-level action control and sandboxing into a coordinated detection net, on top of a traditional
AV product.
This extensive protection scheme may be warranted for a laptop computer frequently operating
in untrusted environments (e.g. on cafe or airport Wi-Fi networks), but the heavy defenses may
take their toll on battery life and noticeably impair the generic responsiveness of the computer as
the HIPS protective component and the traditional AV product check each file on a PC to see if it
is malware against a huge blacklist.
216 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY