Page 274 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 274
Financial Accounting
Notes
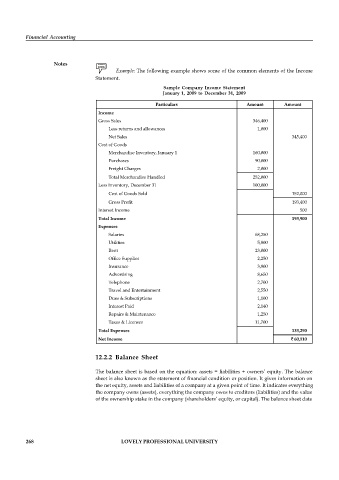
Example: The following example shows some of the common elements of the Income
Statement.
Sample Company Income Statement
January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2009
Particulars Amount Amount
Income
Gross Sales 346,400
Less returns and allowances 1,000
Net Sales 345,400
Cost of Goods
Merchandise Inventory, January 1 160,000
Purchases 90,000
Freight Charges 2,000
Total Merchandise Handled 252,000
Less Inventory, December 31 100,000
Cost of Goods Sold 152,000
Gross Profit 193,400
Interest Income 500
Total Income 193,900
Expenses
Salaries 68,250
Utilities 5,800
Rent 23,000
Office Supplies 2,250
Insurance 3,900
Advertising 8,650
Telephone 2,700
Travel and Entertainment 2,550
Dues & Subscriptions 1,100
Interest Paid 2,140
Repairs & Maintenance 1,250
Taxes & Licenses 11,700
Total Expenses 133,290
Net Income 60,110
12.2.2 Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is based on the equation: assets = liabilities + owners’ equity. The balance
sheet is also known as the statement of financial condition or position. It gives information on
the net equity, assets and liabilities of a company at a given point of time. It indicates everything
the company owns (assets), everything the company owes to creditors (liabilities) and the value
of the ownership stake in the company (shareholders’ equity, or capital). The balance sheet date
268 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY