Page 275 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 275
Unit 12: Corporate Financial Statements
is the ending date of the period or year, and is a continuation of the amounts recorded since the Notes
inception of the company or organization. The balance sheet is a “snapshot” of the financial
position of the company at the balance sheet date and shows the accumulated balance of the
accounts. Assets and liabilities are separated between current and long-term, where current items
are those items, which will be realized or paid, within one year of the balance sheet date. Typical
current assets are cash, prepaid expenses, accounts receivable and inventory. The major categories
reported on the balance sheet include:
Assets are divided into various categories: current assets (including cash or other highly
liquid financial assets, accounts receivable, and the value of inventories), and fixed assets
or investments. The fixed assets item includes the “book” value of the company’s
accumulated purchases of property and equipment: that is, what the company paid for
those assets, less their estimated depreciation over the years they have been used. This
book value may differ from the actual usefulness or resale value of those assets.
Liabilities are also divided into current and long-run. Current liabilities include accounts
payable, and the value of debt and interest on debt that is due within the next year.
Another major liability is the company’s long-term debt (that which comes due later than
one year from the present).
Shareholder’s equity is a special kind of liability. The shareholders’ equity, in essence, is
what the company “owes” to its own shareholders. It is equal to the value of the company’s
assets, minus what the company owes to people or businesses other than its own
shareholders.
Another term for this value is the “net worth” of the company. A company’s shareholders’
equity should (by definition) equal the value of any initial equity funds advanced by the
shareholders (through public offerings of new stock or other financing methods), plus the
cumulative value of the company’s retained earnings (that is, that portion of the company’s past
profits which were not paid back to shareholders in the form of dividends). Because equity is
treated as a liability, the company’s total assets and total liabilities (including shareholders’
equity) are always equal. If a company’s accumulated liabilities (excluding shareholders’ equity)
are greater than its total assets, then shareholders’ equity is negative. Usually, a company will
only have negative shareholders’ equity if it has experienced a string of losses, which have more
than wiped out the value of the equity which shareholders put into the company (through their
initial investments in the company) and any accumulated profits which the company earned in
earlier, happier times. A company with negative equity is usually (but not always) facing a
serious risk of bankruptcy.
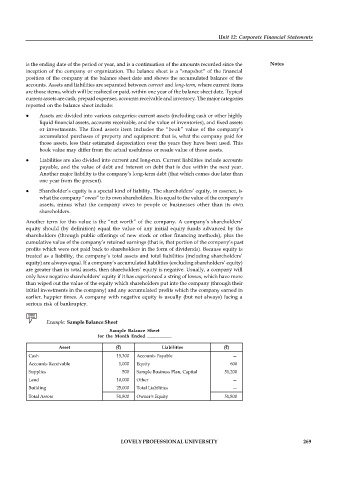
Example: Sample Balance Sheet
Sample Balance Sheet
for the Month Ended __________
Asset ( ) Liabilities ( )
Cash 15,300 Accounts Payable —
Accounts Receivable 1,000 Equity 600
Supplies 500 Sample Business Plan, Capital 51,200
Land 10,000 Other —
Building 25,000 Total Liabilities —
Total Assets 51,800 Owner's Equity 51,800
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 269