Page 77 - DMGT206_PRODUCTION_AND_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 77
Production and Operations Management
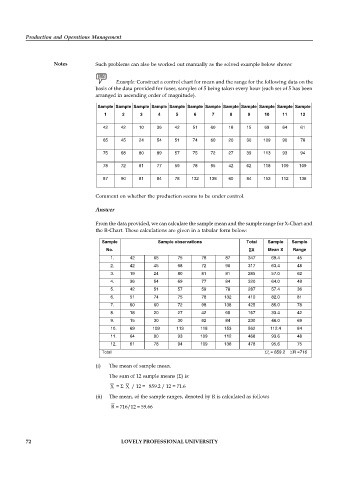
Notes Such problems can also be worked out manually as the solved example below shows:
Example: Construct a control chart for mean and the range for the following data on the
basis of the data provided for fuses, samples of 5 being taken every hour (each set of 5 has been
arranged in ascending order of magnitude).
Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample Sample
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
42 42 10 36 42 51 60 18 15 69 64 61
65 45 24 54 51 74 60 20 30 109 90 78
75 68 80 89 57 75 72 27 39 113 93 94
78 72 81 77 59 78 95 42 62 118 109 109
87 90 81 84 78 132 138 60 84 153 112 136
Comment on whether the production seems to be under control.
Answer
From the data provided, we can calculate the sample mean and the sample range for X-Chart and
the R-Chart. These calculations are given in a tabular form below:
Sample Sample observations Total Sample Sample
No. X Mean X Range
1. 42 65 75 78 87 347 69.4 45
2. 42 45 68 72 90 317 63.4 48
3. 19 24 80 81 81 285 57.0 62
4. 36 54 69 77 84 320 64.0 48
5. 42 51 57 59 78 287 57.4 36
6. 51 74 75 78 132 410 82.0 81
7. 60 60 72 98 138 425 85.0 78
8. 18 20 27 42 60 167 33.4 42
9. 15 30 30 62 84 230 46.0 69
10. 69 109 113 118 153 562 112.4 84
11. 64 90 93 109 112 468 93.6 48
12. 61 78 94 109 136 478 95.6 75
Total = 859.2 R =716
(i) The mean of sample mean.
The sum of 12 sample means () is:
= / 12 = 859.2 / 12 = 71.6
(ii) The mean, of the sample ranges, denoted by R is calculated as follows
= 716/12 = 59.66
72 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY