Page 127 - DMGT302_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 127
Fundamentals of Project Management
Notes However, in Research & Development projects, or in Social Projects which are defined as “Process
Projects”, where learning is an important outcome, the cause-effect relationship is not so well
established. In such situations, the PERT approach is useful, because it can accommodate the
variation in event completion times, based on an expert’s or an expert committee’s estimates.
For each activity, three time estimates are taken
1. The Most Optimistic
2. The Most Likely
3. The Most Pessimistic
The duration of an activity is calculated using the following formula:
t 0 + 4t m + t p
t e =
6
Where t is the Expected time, t is the Optimistic time, t is the most probable activity time and
e o m
t is the Pessimistic time. It is not necessary to go into the theory behind the formula.
p
It is enough to know that the weights are based on an approximation of the Beta distribution.
The Standard Deviation, which is a good measure of the variability of each activity is calculated
by the rather simplified formula:
t + t
S = p 0
1
6
The variance is the square of the standard deviation.
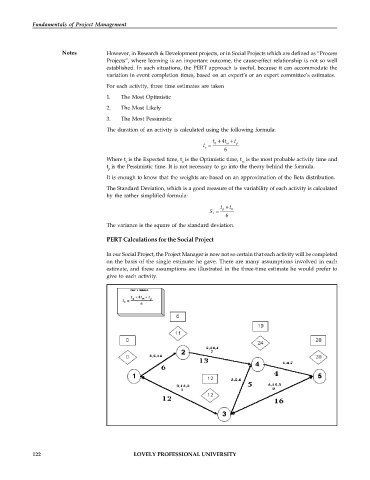
PERT Calculations for the Social Project
In our Social Project, the Project Manager is now not so certain that each activity will be completed
on the basis of the single estimate he gave. There are many assumptions involved in each
estimate, and these assumptions are illustrated in the three-time estimate he would prefer to
give to each activity.
122 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY