Page 130 - DMGT308_CUSTOMER_RELATIONSHIP_MANAGEMENT
P. 130
Unit 5: Closed Loop Marketing
new observations (on specific variables) from other observations (on the same or other variables) Notes
after executing a process of so-called learning from existing data. Neural Networks is one of the
Data Mining techniques.
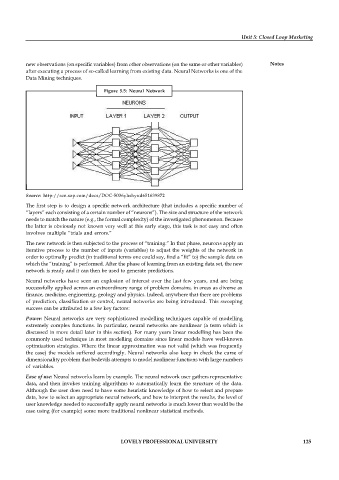
Figure 5.5: Neural Network
Source: http://scn.sap.com/docs/DOC-5036yhshyud651639872
The first step is to design a specific network architecture (that includes a specific number of
“layers” each consisting of a certain number of “neurons”). The size and structure of the network
needs to match the nature (e.g., the formal complexity) of the investigated phenomenon. Because
the latter is obviously not known very well at this early stage, this task is not easy and often
involves multiple “trials and errors.”
The new network is then subjected to the process of “training.” In that phase, neurons apply an
iterative process to the number of inputs (variables) to adjust the weights of the network in
order to optimally predict (in traditional terms one could say, find a “fit” to) the sample data on
which the “training” is performed. After the phase of learning from an existing data set, the new
network is ready and it can then be used to generate predictions.
Neural networks have seen an explosion of interest over the last few years, and are being
successfully applied across an extraordinary range of problem domains, in areas as diverse as
finance, medicine, engineering, geology and physics. Indeed, anywhere that there are problems
of prediction, classification or control, neural networks are being introduced. This sweeping
success can be attributed to a few key factors:
Power: Neural networks are very sophisticated modelling techniques capable of modelling
extremely complex functions. In particular, neural networks are nonlinear (a term which is
discussed in more detail later in this section). For many years linear modelling has been the
commonly used technique in most modelling domains since linear models have well-known
optimization strategies. Where the linear approximation was not valid (which was frequently
the case) the models suffered accordingly. Neural networks also keep in check the curse of
dimensionality problem that bedevils attempts to model nonlinear functions with large numbers
of variables.
Ease of use: Neural networks learn by example. The neural network user gathers representative
data, and then invokes training algorithms to automatically learn the structure of the data.
Although the user does need to have some heuristic knowledge of how to select and prepare
data, how to select an appropriate neural network, and how to interpret the results, the level of
user knowledge needed to successfully apply neural networks is much lower than would be the
case using (for example) some more traditional nonlinear statistical methods.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 125