Page 133 - DMGT308_CUSTOMER_RELATIONSHIP_MANAGEMENT
P. 133
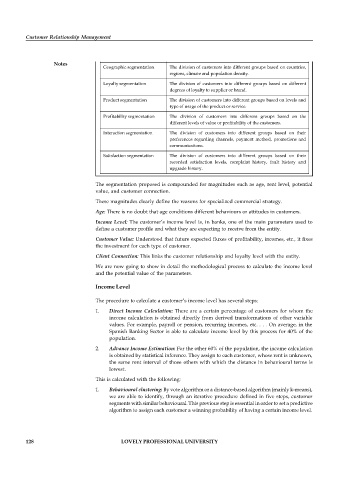
Segment definition
Segmentation type
The division of prospects and customers into groups reflecting the
Buyer-readiness segmentation
different stages which consumers normally pass through during the
purchase process. These usually comprise ignorance, awareness,
knowledge, preference and conviction.
Dividing the market into groups according to the different benefits
Benefit segmentation
that consumers seek from the product.
Occasion segmentation
The division of customers into groups which consume a product or
service at particular times, in certain situations, in response to
particular events or according to seasonal or cyclical times.
Psychographic/lifestyle The division of customers into groups based on lifestyle, social
segmentation behaviour, values, sensitivities and personality characteristics.
Demographic segmentation The division of customers into different groups based on
demographic variables such as age, gender, family size, income,
Customer Relationship Management
occupation, education, language, religion, race and nationality.
Life-cycle segmentation The division of customers into different groups that recognise the
different needs of consumers at different stages in their life.
Notes
Geographic segmentation The division of customers into different groups based on countries,
regions, climate and population density.
Loyalty segmentation The division of customers into different groups based on different
degrees of loyalty to supplier or brand.
Product segmentation The division of customers into different groups based on levels and
type of usage of the product or service.
Profitability segmentation The division of customers into different groups based on the
different levels of value or profitability of the customers.
Interaction segmentation The division of customers into different groups based on their
preferences regarding channels, payment method, promotions and
communications.
Satisfaction segmentation The division of customers into different groups based on their
recorded satisfaction levels, complaint history, fault history and
upgrade history.
The segmentation proposed is compounded for magnitudes such as age, rent level, potential
value, and customer connection.
These magnitudes clearly define the reasons for specialized commercial strategy.
Age: There is no doubt that age conditions different behaviours or attitudes in customers.
Income Level: The customer’s income level is, in banks, one of the main parameters used to
define a customer profile and what they are expecting to receive from the entity.
Customer Value: Understood that future expected fluxes of profitability, incomes, etc., it fixes
the investment for each type of customer.
Client Connection: This links the customer relationship and loyalty level with the entity.
We are now going to show in detail the methodological process to calculate the income level
and the potential value of the parameters.
Income Level
The procedure to calculate a customer’s income level has several steps:
1. Direct Income Calculation: There are a certain percentage of customers for whom the
income calculation is obtained directly from derived transformations of other variable
values. For example, payroll or pension, recurring incomes, etc. . . . On average, in the
Spanish Banking Sector is able to calculate income level by this process for 40% of the
population.
2. Advance Income Estimation: For the other 60% of the population, the income calculation
is obtained by statistical inference. They assign to each customer, whose rent is unknown,
the same rent interval of those others with which the distance in behavioural terms is
lowest.
This is calculated with the following:
1. Behavioural clustering: By vote algorithm or a distance-based algorithm (mainly k-means),
we are able to identify, through an iterative procedure defined in five steps, customer
segments with similar behavioural. This previous step is essential in order to set a predictive
algorithm to assign each customer a winning probability of having a certain income level.
128 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY