Page 82 - DMGT402_MANAGEMENT_PRACTICES_AND_ORGANIZATIONAL_BEHAVIOUR
P. 82
Unit 3: Planning and Decision-making
another square. Squares represent decisions, circles represent uncertainty or random factors. Notes
Write the decision or factor to be considered above the square or circle. If you have completed
the solution at the end of the line, just leave it blank.
Starting from the new decision squares on your diagram, draw out lines representing the options
that could be taken. From the circles draw out lines representing possible outcomes. Again
mark a brief note on the line saying what it means. Keep on doing this until you have drawn
down as many of the possible outcomes and decisions as you can see leading on from your
original decision.
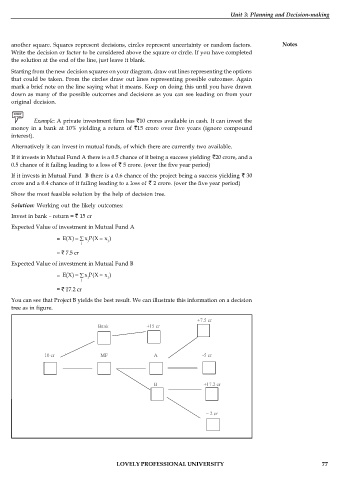
Example: A private investment firm has 10 crores available in cash. It can invest the
money in a bank at 10% yielding a return of 15 crore over five years (ignore compound
interest).
Alternatively it can invest in mutual funds, of which there are currently two available.
If it invests in Mutual Fund A there is a 0.5 chance of it being a success yielding 20 crore, and a
0.5 chance of it failing leading to a loss of 5 crore. (over the five year period)
If it invests in Mutual Fund B there is a 0.6 chance of the project being a success yielding 30
crore and a 0.4 chance of it failing leading to a loss of 2 crore. (over the five year period)
Show the most feasible solution by the help of decision tree.
Solution: Working out the likely outcomes:
Invest in bank – return = 15 cr
Expected Value of investment in Mutual Fund A
= E(X) x P(X x )
j
j
j
= 7.5 cr
Expected Value of investment in Mutual Fund B
= E(X) x P(X x )
j
j
j
= 17.2 cr
You can see that Project B yields the best result. We can illustrate this information on a decision
tree as in figure.
+7.5 cr
Bank +15 cr
10 cr ` MF A -5 cr
B +17.2 cr
– 2 cr
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 77