Page 170 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 170
Inflow cash ( ) Outflow cash ( )
Opening cash balance XXXX Redemption of preference shares XXXX
Cash from in operations XXXX Redemption of debentures XXXX
Sale of assets XXXX Repayment of loans XXXX
Unit 8: Cash Flow Statement
Issue of shares XXXX Payment of dividends XXXX
Issue of debentures XXXX Payment of tax XXXX
Raising of loans XXXX Cash lost in operations XXXX
Notes
Collection from debentures XXXX
Refund of tax XXXX
XXXX XXXX
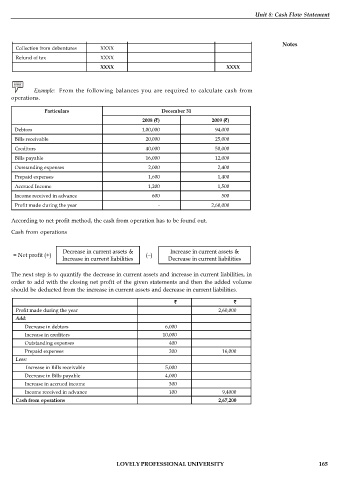
Example: From the following balances you are required to calculate cash from
operations.
Particulars December 31
2008 ( ) 2009 ( )
Debtors 1,00,000 94,000
Bills receivable 20,000 25,000
Creditors 40,000 50,000
Bills payable 16,000 12,000
Outstanding expenses 2,000 2,400
Prepaid expenses 1,600 1,400
Accrued Income 1,200 1,500
Income received in advance 600 500
Profit made during the year - 2,60,000
According to net profit method, the cash from operation has to be found out.
Cash from operations
Decrease in current assets & Increase in current assets &
= Net profit (+) (–)
Increase in current liabilities Decrease in current liabilities
The next step is to quantify the decrease in current assets and increase in current liabilities, in
order to add with the closing net profit of the given statements and then the added volume
should be deducted from the increase in current assets and decrease in current liabilities.
Profit made during the year 2,60,000
Add:
Decrease in debtors 6,000
Increase in creditors 10,000
Outstanding expenses 400
Prepaid expenses 200 16,000
Less:
Increase in Bills receivable 5,000
Decrease in Bills payable 4,000
Increase in accrued income 300
Income received in advance 100 9,4000
Cash from operations 2,67,200
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 165