Page 173 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 173
Accounting for Managers
Notes
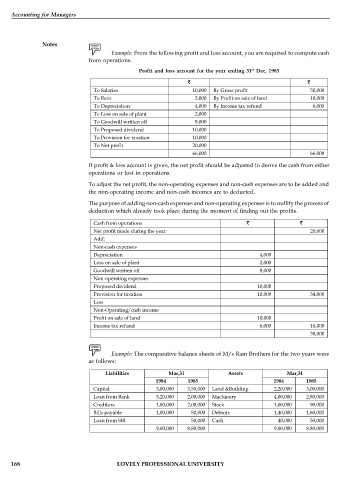
Example: From the following profit and loss account, you are required to compute cash
from operations.
st
Profit and loss account for the year ending 31 Dec, 1983
To Salaries 10,000 By Gross profit 50,000
To Rent 2,000 By Profit on sale of land 10,000
To Depreciation 4,000 By Income tax refund 6,000
To Loss on sale of plant 2,000
To Goodwill written off 8,000
To Proposed dividend 10,000
To Provision for taxation 10,000
To Net profit 20,000
66,000 66,000
If profit & loss account is given, the net profit should be adjusted to derive the cash from either
operations or lost in operations.
To adjust the net profit, the non-operating expenses and non-cash expenses are to be added and
the non-operating income and non-cash incomes are to deducted.
The purpose of adding non-cash expenses and non-operating expenses is to nullify the process of
deduction which already took place during the moment of finding out the profits.
Cash from operations
Net profit made during the year 20,000
Add:
Non-cash expenses
Depreciation 4,000
Loss on sale of plant 2,000
Goodwill written off 8,000
Non-operating expenses
Proposed dividend 10,000
Provision for taxation 10,000 34,000
Less
Non-Operating/cash income
Profit on sale of land 10,000
Income tax refund 6,000 16,000
38,000
Example: The comparative balance sheets of M/s Ram Brothers for the two years were
as follows:
Liabilities Mar,31 Assets Mar,31
1984 1985 1984 1985
Capital 3,00,000 3,50,000 Land &Building 2,20,000 3,00,000
Loan from Bank 3,20,000 2,00,000 Machinery 4,00,000 2,80,000
Creditors 1,80,000 2,00,000 Stock 1,00,000 90.000
Bills payable 1,00,000 80,000 Debtors 1,40,000 1,60,000
Loan from SBI 50,000 Cash 40,000 50,000
9,00,000 8,80,000 9,00,000 8,80,000
168 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY