Page 200 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 200
Unit 9: Budgetary Control
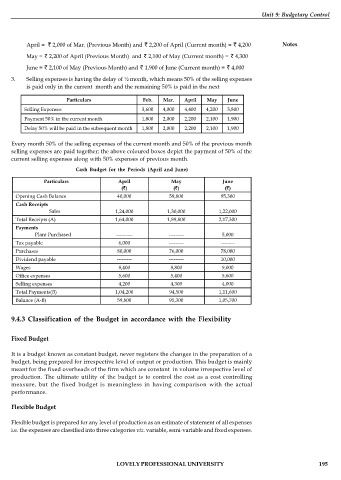
April = 2,000 of Mar. (Previous Month) and 2,200 of April (Current month) = 4,200 Notes
May = 2,200 of April (Previous Month) and 2,100 of May (Current month) = 4,300
June = 2,100 of May (Previous Month) and 1,900 of June (Current month) = 4,000
3. Selling expenses is having the delay of ½ month, which means 50% of the selling expenses
is paid only in the current month and the remaining 50% is paid in the next
Particulars Feb. Mar. April May June
Selling Expenses 3,600 4,000 4,400 4,200 3,800
Payment 50% in the current month 1,800 2,000 2,200 2,100 1,900
Delay 50% will be paid in the subsequent month 1,800 2,000 2,200 2,100 1,900
Every month 50% of the selling expenses of the current month and 50% of the previous month
selling expenses are paid together; the above coloured boxes depict the payment of 50% of the
current selling expenses along with 50% expenses of previous month.
Cash Budget for the Periods (April and June)
Particulars April May June
( ) ( ) ( )
Opening Cash Balance 40,000 59,800 95,300
Cash Receipts
Sales 1,24,000 1,30,000 1,22,000
Total Receipts (A) 1,64,000 1,89,800 2,17,300
Payments
Plant Purchased ---------- --------- 5,000
Tax payable 6,000 --------- --------
Purchases 80,000 76,000 78,000
Dividend payable --------- --------- 10,000
Wages 8,400 8,800 9,000
Office expenses 5,600 5,400 5,600
Selling expenses 4,200 4,300 4,000
Total Payments(B) 1,04,200 94,500 1,11,600
Balance (A-B) 59,800 95,300 1,05,700
9.4.3 Classification of the Budget in accordance with the Flexibility
Fixed Budget
It is a budget known as constant budget, never registers the changes in the preparation of a
budget, being prepared for irrespective level of output or production. This budget is mainly
meant for the fixed overheads of the firm which are constant in volume irrespective level of
production. The ultimate utility of the budget is to control the cost as a cost controlling
measure, but the fixed budget is meaningless in having comparison with the actual
performance.
Flexible Budget
Flexible budget is prepared for any level of production as an estimate of statement of all expenses
i.e. the expenses are classified into three categories viz. variable, semi-variable and fixed expenses.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 195