Page 202 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 202
Particulars
Variable overheads
Indirect labour 70% capacity 80% capacity 90% capacity
24,000
27,000
21,000
Stores including spares 7,000 8,000 9,000
Semi-variable Expenses - Power*
Fixed 30% 8,000 8,000 8,000
**Variable 70%
28,000 32,000 36,000 Unit 9: Budgetary Control
Repairs and mainternance
***Fixed 80% 3,200 3,200 3,200
****Variable 20% 700 800 900
Notes
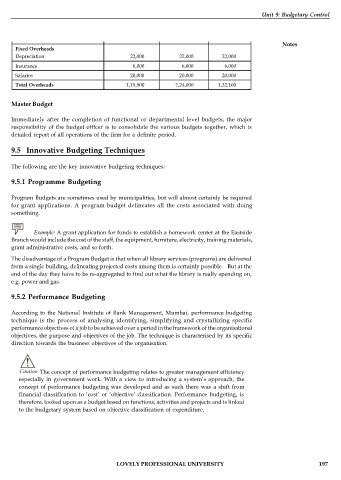
Fixed Overheads
Depreciation 22,000 22,000 22,000
Insurance 6,000 6,000 6,000
Salaries 20,000 20,000 20,000
Total Overheads 1,15,900 1,24,000 1,32,100
Master Budget
Immediately after the completion of functional or departmental level budgets, the major
responsibility of the budget officer is to consolidate the various budgets together, which is
detailed report of all operations of the firm for a definite period.
9.5 Innovative Budgeting Techniques
The following are the key innovative budgeting techniques:
9.5.1 Programme Budgeting
Program Budgets are sometimes used by municipalities, but will almost certainly be required
for grant applications. A program budget delineates all the costs associated with doing
something.
Example: A grant application for funds to establish a homework center at the Eastside
Branch would include the cost of the staff, the equipment, furniture, electricity, training materials,
grant administrative costs, and so forth.
The disadvantage of a Program Budget is that when all library services (programs) are delivered
from a single building, delineating projected costs among them is certainly possible. But at the
end of the day they have to be re-aggregated to find out what the library is really spending on,
e.g. power and gas.
9.5.2 Performance Budgeting
According to the National Institute of Bank Management, Mumbai, performance budgeting
technique is the process of analysing identifying, simplifying and crystallizing specific
performance objectives of a job to be achieved over a period in the framework of the organisational
objectives, the purpose and objectives of the job. The technique is characterised by its specific
direction towards the business objectives of the organisation.
!
Caution The concept of performance budgeting relates to greater management efficiency
especially in government work. With a view to introducing a system’s approach, the
concept of performance budgeting was developed and as such there was a shift from
financial classification to ‘cost’ or ‘objective’ classification. Performance budgeting, is
therefore, looked upon as a budget based on functions, activities and projects and is linked
to the budgetary system based on objective classification of expenditure.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 197