Page 250 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 250
Unit 11: Variance Analysis
11. Which of the following cannot be included among the reasons of variance Notes
(a) Price increase
(b) Use of workers at rate of pay lower than standard
(c) Lost time in excess of standard allowed
(d) None of these
11.9 Review Questions
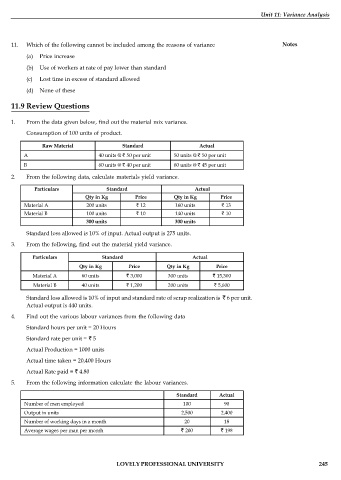
1. From the data given below, find out the material mix variance.
Consumption of 100 units of product.
Raw Material Standard Actual
A 40 units @ 50 per unit 50 units @ 50 per unit
B 60 units @ 40 per unit 60 units @ 45 per unit
2. From the following data, calculate materials yield variance.
Particulars Standard Actual
Qty in Kg Price Qty in Kg Price
Material A 200 units 12 160 units 13
Material B 100 units 10 140 units 10
300 units 300 units
Standard loss allowed is 10% of input. Actual output is 275 units.
3. From the following, find out the material yield variance.
Particulars Standard Actual
Qty in Kg Price Qty in Kg Price
Material A 60 units 3,000 300 units 15,300
Material B 40 units 1,200 200 units 5,600
Standard loss allowed is 10% of input and standard rate of scrap realization is 6 per unit.
Actual output is 440 units.
4. Find out the various labour variances from the following data
Standard hours per unit = 20 Hours
Standard rate per unit = 5
Actual Production = 1000 units
Actual time taken = 20,400 Hours
Actual Rate paid = 4.80
5. From the following information calculate the labour variances.
Standard Actual
Number of men employed 100 90
Output in units 2,500 2,400
Number of working days in a month 20 18
Average wages per man per month 200 198
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 245