Page 146 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 146
Research Methodology
Notes a class will be equal to the mean of observations in that class and hence can be taken as
their representative. Therefore, if Xi is the mid-value of ith class with frequency fi, the
above assumption implies that there are fi observations each with magnitude Xi (i = 1 to n).
Thus, the arithmetic mean of a grouped frequency distribution can also be calculated by
the use of the formula.
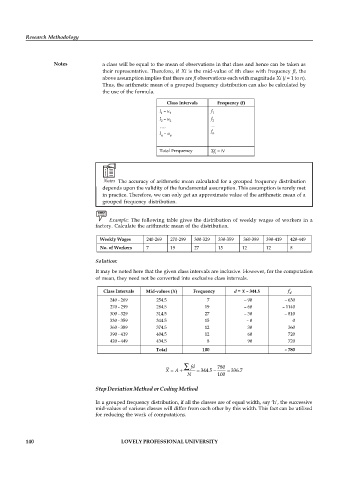
Class Intervals Frequency (f)
l – u f
1 1 1
l – u f
2 2 2
…. ….
f
l – u n
n
n
Total Frequency f = N
i
Notes The accuracy of arithmetic mean calculated for a grouped frequency distribution
depends upon the validity of the fundamental assumption. This assumption is rarely met
in practice. Therefore, we can only get an approximate value of the arithmetic mean of a
grouped frequency distribution.
Example: The following table gives the distribution of weekly wages of workers in a
factory. Calculate the arithmetic mean of the distribution.
Weekly Wages 240-269 270-299 300-329 330-359 360-389 390-419 420-449
No. of Workers 7 19 27 15 12 12 8
Solution:
It may be noted here that the given class intervals are inclusive. However, for the computation
of mean, they need not be converted into exclusive class intervals.
Class Intervals Mid-values (X) Frequency d = X – 344.5 f
d
240 - 269 254.5 7 – 90 – 630
270 - 299 284.5 19 – 60 – 1140
300 - 329 314.5 27 – 30 – 810
330 - 359 344.5 15 – 0 0
360 - 389 374.5 12 30 360
390 - 419 404.5 12 60 720
420 - 449 434.5 8 90 720
Total 100 – 780
fd 780
X A 344.5 336.7
N 100
Step Deviation Method or Coding Method
In a grouped frequency distribution, if all the classes are of equal width, say ‘h’, the successive
mid-values of various classes will differ from each other by this width. This fact can be utilised
for reducing the work of computations.
140 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY