Page 148 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 148
Research Methodology
Notes mean wage of the workers of a factory, it would be wrong to compute simple arithmetic mean
if there are a few workers (say managers) with very high wages while majority of the workers
are at low level of wages. The simple arithmetic mean, in such a situation, will give a higher
value that cannot be regarded as representative wage for the group. In order that the mean wage
gives a realistic picture of the distribution, the wages of managers should be given less importance
in its computation. The mean calculated in this manner is called weighted arithmetic mean. The
computation of weighted arithmetic is useful in many situations where different items are of
unequal importance, e.g., the construction index numbers, computation of standardised death
and birth rates, etc.
Formulae for Weighted Arithmetic Mean
Let X , X ....., X be n values with their respective weights w , w ....., w . Their weighted
1 2 n 1 2 n
arithmetic mean denoted as is given by,
i w X i
1. X w i w (Using direct method),
w i i d
2. X w A i w (where di = Xi – A) (Using shortcut method),
i w u i i X – A
3. X w A i w h where u h (Using step-deviation method)
i
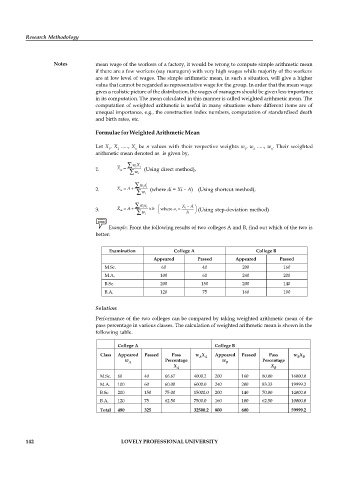
Example: From the following results of two colleges A and B, find out which of the two is
better:
Examination College A College B
Appeared Passed Appeared Passed
M.Sc. 60 40 200 160
M.A. 100 60 240 200
B.Sc. 200 150 200 140
B.A. 120 75 160 100
Solution:
Performance of the two colleges can be compared by taking weighted arithmetic mean of the
pass percentage in various classes. The calculation of weighted arithmetic mean is shown in the
following table.
College A College B
Class Appeared Passed Pass w X Appeared Passed Pass w X
B
B
A
A
w Percentage w Percentage
A B
X X
A B
M.Sc. 60 40 66.67 4000.2 200 160 80.00 16000.0
M.A. 100 60 60.00 6000.0 240 200 83.33 19999.2
B.Sc. 200 150 75.00 15000.0 200 140 70.00 14000.0
B.A. 120 75 62.50 7500.0 160 100 62.50 10000.0
Total 480 325 32500.2 800 600 59999.2
142 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY