Page 183 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 183
Unit 9: Correlation and Regression
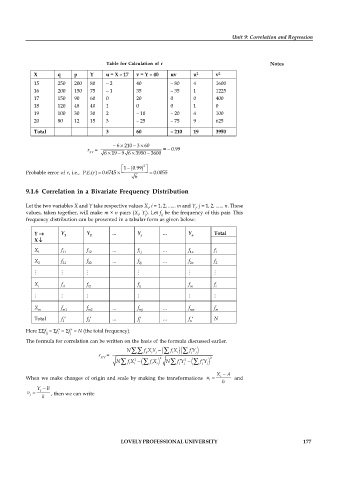
Table for Calculation of r Notes
2
2
X q p Y u = X – 17 v = Y – 40 uv u v
15 250 200 80 – 2 40 – 80 4 1600
16 200 150 75 – 1 35 – 35 1 1225
17 150 90 60 0 20 0 0 400
18 120 48 40 1 0 0 1 0
19 100 30 30 2 – 10 – 20 4 100
20 80 12 15 3 – 25 – 75 9 625
Total 3 60 – 210 19 3950
- 6 210 3 60
´
´
-
r = = - 0.99
-
´
´
-
XY 6 19 9 6 3950 3600
)
2
Probable error of r, i.e., . .( )P E r = 0.6745 ´ ë 1 é - (0.99 ù û = 0.0055
6
9.1.6 Correlation in a Bivariate Frequency Distribution
Let the two variables X and Y take respective values X , i = 1, 2, ...... m and Y , j = 1, 2, ...... n. These
i j
values, taken together, will make m × n pairs (X , Y ). Let f be the frequency of this pair. This
i j ij
frequency distribution can be presented in a tabular form as given below:
Y Y Y ... Y ... Y Total
1
n
2
j
X
X f f ... f ... f f
1 11 12 1j 1n 1
X f f ... f ... f f
2 21 22 2j 2n 2
X f f f f f
i i1 i2 ij in i
X f f ... f ... f f
m m1 m2 mj mn m
Total f f ... f ... f N
1 2 j n
Here f = f = f = N (the total frequency).
ij i j
The formula for correlation can be written on the basis of the formula discussed earlier.
N åå f X Y - (å f X )(å f Y )
r = ij i j i i j j
XY 2 2
N å f X - (å f X ) N å f Y - (å f Y )
2
2
i i i i j j j j
X - A
When we make changes of origin and scale by making the transformations u = i and
i
h
Y - B
v = j
j , then we can write
k
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 177