Page 116 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 116
Operations Management
Notes There are occasions when effectiveness and efficiency can be increased by deviating from
procedures. For example, we can look at task sharing i.e., when more than one workstation is
manned by one worker. This can reduce idleness as we are eliminating workers, and letting the
others take turns at a workstation: other improvements are possible if more than one worker
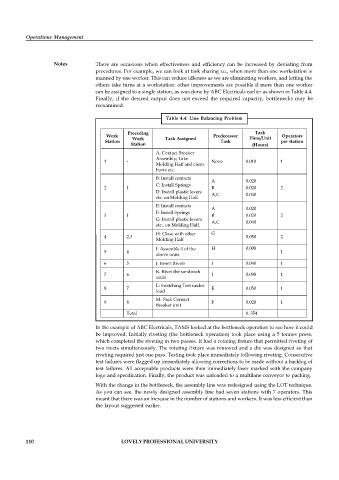
can be assigned to a single station, as was done by ABC Electricals earlier as shown in Table 4.4.
Finally, if the desired output does not exceed the required capacity, bottlenecks may be
reexamined.
Table 4.4: Line Balancing Problem
Preceding Task
Work Predecessor Time/Unit Operators
Station Work Task Assigned Task per station
Station (Hours)
A: Contact Breaker
Assembly; Take
1 - None 0.010 1
Molding Half and clean
burrs etc.
B: Install contacts
A 0.020
C: Install Springs
2 1 B 0.020 2
D: Install plastic levers A,C 0.040
etc. on Molding Half.
E: Install contacts
A 0.020
F: Install Springs
3 1 B 0.020 2
G: Install plastic levers A,C 0.040
etc., on Molding Half.
H: Close with other G
4 2,3 0.050 2
Molding Half
I: Assemble 4 of the H 0.008
5 4 1
above units
6 5 J: Insert Rivets I 0.040 1
K: Rivet the sandwich
7 6 J 0.098 1
units
L: Switching Test under
8 7 E 0.050 1
load
M: Pack Contact
9 8 F 0.020 1
Breaker unit
Total 0. 354
In the example of ABC Electricals, TAMS looked at the bottleneck operation to see how it could
be improved. Initially riveting (the bottleneck operation) took place using a 5 tonnes press,
which completed the riveting in two passes. It had a rotating fixture that permitted riveting of
two rivets simultaneously. The rotating fixture was removed and a die was designed so that
riveting required just one pass. Testing took place immediately following riveting. Consecutive
test failures were flagged up immediately allowing corrections to be made without a backlog of
test failures. All acceptable products were then immediately laser marked with the company
logo and specification. Finally, the product was unloaded to a multilane conveyor to packing.
With the change in the bottleneck, the assembly line was redesigned using the LOT technique.
As you can see, the newly designed assembly line had seven stations with 7 operators. This
meant that there was an increase in the number of stations and workers. It was less efficient than
the layout suggested earlier.
110 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY