Page 269 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 269
Unit 12: Service Level Method of Determining Q – ABC Classification
The next 30 percent of the items are classified as ‘B’ items. These deserve less attention than ‘A’ Notes
items. Finally, the last 50 percent of items are ‘C’ items. These have the lowest rupee usage and
can be monitored loosely, with larger safety stocks maintained to avoid stock outs. They should
have carefully established but routine controls.
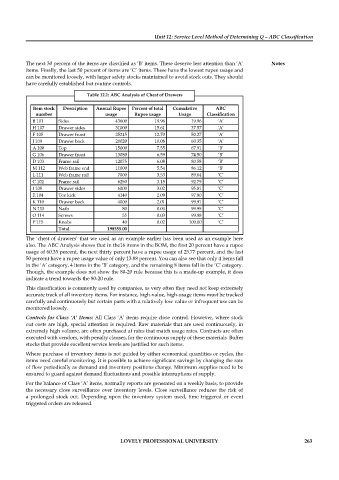
Table 12.1: ABC Analysis of Chest of Drawers
Item stock Description Annual Rupee Percent of total Cumulative ABC
number usage Rupee usage Usage Classification
B 101 Sides 43600 19.96 19.96 ‘A’
H 107 Drawer sides 31000 15.61 37.57 ‘A’
F 105 Drawer front 25215 12.70 50.27 ‘A’
J 109 Drawer back 20020 10.08 60.35 ‘A’
A 100 Top 15000 7.55 67.91 ‘B’
G 106 Drawer front 13080 6.59 74.50 ‘B’
D 103 Frame rail 12075 6.08 80.58 ‘B’
M 112 Web frame end 11000 5.54 86.12 ‘B’
L 111 Web frame rail 7000 3.53 89.64 ‘C’
C 102 Frame rail 6250 3.15 92.79 ‘C’
I 108 Drawer sides 6000 3.02 95.81 ‘C’
E 104 Toe kick 4140 2.09 97.90 ‘C’
K 110 Drawer back 4000 2.01 99.91 ‘C’
N 113 Nails 80 0.04 99.95 ‘C’
O 114 Screws 55 0.03 99.98 ‘C’
P 115 Knobs 40 0.02 100.00 ‘C’
Total 198555.00
The ‘chest of drawers’ that we used as an example earlier has been used as an example here
also. The ABC Analysis shows that in the16 items in the BOM, the first 20 percent have a rupee
usage of 60.35 percent, the next thirty percent have a rupee usage of 25.77 percent, and the last
50 percent have a rupee usage value of only 13.88 percent. You can also see that only 4 items fall
in the ‘A’ category, 4 items in the ‘B’ category, and the remaining 8 items fall in the ‘C’ category.
Though, the example does not show the 80-20 rule because this is a made-up example, it does
indicate a trend towards the 80-20 rule.
This classification is commonly used by companies, as very often they need not keep extremely
accurate track of all inventory items. For instance, high-value, high-usage items must be tracked
carefully and continuously but certain parts with a relatively low value or infrequent use can be
monitored loosely.
Controls for Class ‘A’ Items: All Class ‘A’ items require close control. However, where stock
out costs are high, special attention is required. Raw materials that are used continuously, in
extremely high volume, are often purchased at rates that match usage rates. Contracts are often
executed with vendors, with penalty clauses, for the continuous supply of these materials. Buffer
stocks that provide excellent service levels are justified for such items.
Where purchase of inventory items is not guided by either economical quantities or cycles, the
items need careful monitoring. It is possible to achieve significant savings by changing the rate
of flow periodically as demand and inventory positions change. Minimum supplies need to be
ensured to guard against demand fluctuations and possible interruptions of supply.
For the balance of Class ‘A’ items, normally reports are generated on a weekly basis, to provide
the necessary close surveillance over inventory levels. Close surveillance reduces the risk of
a prolonged stock out. Depending upon the inventory system used, time triggered or event
triggered orders are released.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 263