Page 270 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 270
Operations Management
Notes Control for Class ‘B’ Items: These items are generally monitored and controlled by a computer-
based exception reporting system. Periodic review by the management is necessary, but model
parameters are reviewed less often than with Class A items. Normally, stock out costs for Class
B items should be moderate to low, and buffer stocks should provide adequate control for stock
outs, even though the ordering may occur less often.
However, for items that are scarce, lead time analysis and purchasing strategies can be critical.
This is also true for a number of items that may have to be imported and in addition to
normal transportation times, time required for clearance through customs may not be highly
predictable.
Controls for Class ‘C’ items: Class C items account for the bulk of inventory items. In many
cases, reorder point system is designed in such a way that it does not require a physical stock
evaluation, for example using a “two-bin” system. The inventory is physically separated into two
bins one of which contains an amount equal to the reorder inventory level. Stock is drawn from
the second bin. For each item, action is triggered when the bin gets empty.
Routine controls adequately cover the requirements for this class of inventory. Semiannual or
annual review of the system parameters should be performed to update usage rates, reestablish
supply lead times, and the reorder points. Cost savings might result in changes in EOQ, but they
may not be significant.
12.2 Other Classification Systems
Material items are classified based upon their commercial importance, demand patterns (regular,
sporadic etc.) and supply reliability (of both raw material suppliers and own manufacturing),
etc.
Most of these systems operate in a similar manner to the ABC Classification. A brief description
and comparison of these classifications are given in Table 12.2.
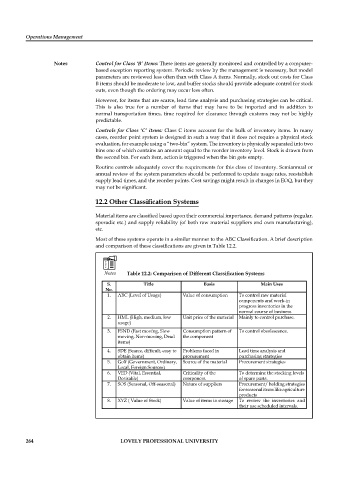
Table 12.2: Comparison of Different Classification Systems
S. Title Basis Main Uses
No.
1. ABC (Level of Usage) Value of consumption To control raw material
components and work-in
progress inventories in the
normal course of business
2. HML (High, medium, low Unit price of the material Mainly to control purchase.
usage)
3. FSND (Fast moving, Slow Consumption pattern of To control obsolescence.
moving, Non-moving, Dead the component
items)
4. SDE (Scarce, difficult, easy to Problems faced in Lead time analysis and
obtain items) procurement purchasing strategies
5. Golf (Government, Ordinary, Source of the material Procurement strategies
Local, Foreign Sources)
6. VED (Vital, Essential, Criticality of the To determine the stocking levels
Desirable) component of spare parts.
7. SOS (Seasonal, Off-seasonal) Nature of suppliers Procurement/ holding strategies
for seasonal items like agriculture
products
8. XYZ ( Value of Stock) Value of items in storage To review the inventories and
their use scheduled intervals.
264 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY