Page 81 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 81
Unit 3: Capacity Planning
Expand, Strong growth = 150 × 5 – 80 = 670 Notes
Expand, Weak growth = 90 × 5 – 80 = 370
Wait, strong, expand = 60 +150 × 4 – 90 = 570
Wait, weak, expand = 60 + 90 × 4 – 90 = 330
Wait, lie low, do nothing = 60 × 5 = 300
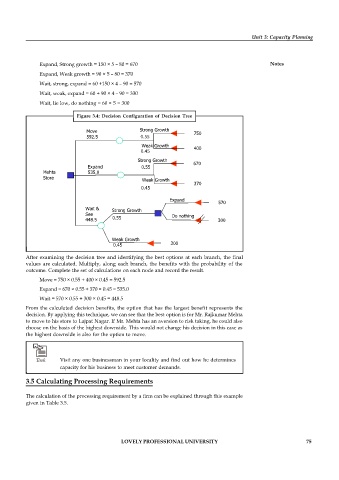
Figure 3.4: Decision Configuration of Decision Tree
Move Strong Growth 750
592.5 0.55
Weak Growth 400
0.45
Strong Growth
670
Expand 0.55
Mehta 535.0
Store Weak Growth
370
0.45
Expand 570
Wait &
Strong Growth
See Do nothing
448.5 0.55 300
Weak Growth
0.45 300
After examining the decision tree and identifying the best options at each branch, the final
values are calculated. Multiply, along each branch, the benefits with the probability of the
outcome. Complete the set of calculations on each node and record the result.
Move = 750 × 0.55 + 400 × 0.45 = 592.5
Expand = 670 × 0.55 + 370 × 0.45 = 535.0
F
Wait = 570 × 0.55 + 300 × 0.45 = 448.5
From the calculated decision benefits, the option that has the largest benefit represents the
decision. By applying this technique, we can see that the best option is for Mr. Rajkumar Mehta
to move to his store to Lajpat Nagar. If Mr. Mehta has an aversion to risk taking, he could also
choose on the basis of the highest downside. This would not change his decision in this case as
the highest downside is also for the option to move.
Task Visit any one businessman in your locality and find out how he determines
capacity for his business to meet customer demands.
3.5 Calculating Processing Requirements
The calculation of the processing requirement by a firm can be explained through this example
given in Table 3.5.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 75