Page 137 - DMGT506_CONSUMER_BEHAVIOUR
P. 137
Consumer Behaviour
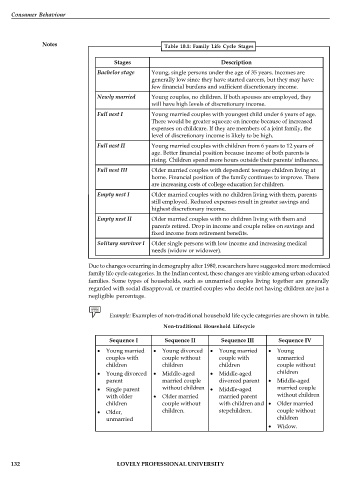
Notes Table 10.1: Family Life Cycle Stages
Stages Description
Bachelor stage Young, single persons under the age of 35 years. Incomes are
generally low since they have started careers, but they may have
few financial burdens and sufficient discretionary income.
Newly married Young couples, no children. If both spouses are employed, they
will have high levels of discretionary income.
Full nest I Young married couples with youngest child under 6 years of age.
There would be greater squeeze on income because of increased
expenses on childcare. If they are members of a joint family, the
level of discretionary income is likely to be high.
Full nest II Young married couples with children from 6 years to 12 years of
age. Better financial position because income of both parents is
rising. Children spend more hours outside their parents' influence.
Full nest III Older married couples with dependent teenage children living at
home. Financial position of the family continues to improve. There
are increasing costs of college education for children.
Empty nest I Older married couples with no children living with them, parents
still employed. Reduced expenses result in greater savings and
highest discretionary income.
Empty nest II Older married couples with no children living with them and
parents retired. Drop in income and couple relies on savings and
fixed income from retirement benefits.
Solitary survivor I Older single persons with low income and increasing medical
needs (widow or widower).
Due to changes occurring in demography after 1980, researchers have suggested more modernised
family life cycle categories. In the Indian context, these changes are visible among urban educated
families. Some types of households, such as unmarried couples living together are generally
regarded with social disapproval, or married couples who decide not having children are just a
negligible percentage.
Example: Examples of non-traditional household life cycle categories are shown in table.
Non-traditional Household Lifecycle
Sequence I Sequence II Sequence III Sequence IV
Young married Young divorced Young married Young
couples with couple without couple with unmarried
children children children couple without
Young divorced Middle-aged Middle-aged children
parent married couple divorced parent Middle-aged
Single parent without children Middle-aged married couple
with older Older married married parent without children
children couple without with children and Older married
Older, children. stepchildren. couple without
unmarried children
Widow.
132 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY