Page 223 - DMGT521_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 223
Project Management
Notes
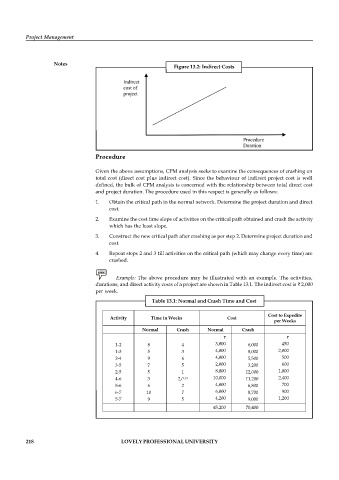
Figure 13.2: Indirect Costs
Procedure
Given the above assumptions, CPM analysis seeks to examine the consequences of crashing on
total cost (direct cost plus indirect cost). Since the behaviour of indirect project cost is well
defined, the bulk of CPM analysis is concerned with the relationship between total direct cost
and project duration. The procedure used in this respect is generally as follows:
1. Obtain the critical path in the normal network. Determine the project duration and direct
cost.
2. Examine the cost time slope of activities on the critical path obtained and crash the activity
which has the least slope.
3. Construct the new critical path after crashing as per step 2. Determine project duration and
cost.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 till activities on the critical path (which may change every time) are
crashed.
Example: The above procedure may be illustrated with an example. The activities,
durations, and direct activity costs of a project are shown in Table 13.1. The indirect cost is 2,000
per week.
Table 13.1: Normal and Crash Time and Cost
Cost to Expedite
Activity Time in Weeks Cost
per Weeks
Normal Crash Normal Crash
1-2 8 4 3,000 6,000 450
1-3 5 3 4,000 8,000 2,000
2-4 9 6 4,000 5,500 500
3-5 7 5 2,000 3,200 600
2-5 5 1 8,000 12,000 1,000
4-6 3 2/ 1/2 10,000 11,200 2,400
5-6 6 2 4,000 6,800 700
6-7 10 7 6,000 8,700 900
5-7 9 5 4,200 9,000 1,200
45,200 70,400
218 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY