Page 294 - DMGT546_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_PROCEDURE_AND_DOCUMENTATION
P. 294
Unit 14: Information Technology in International Business
Notes
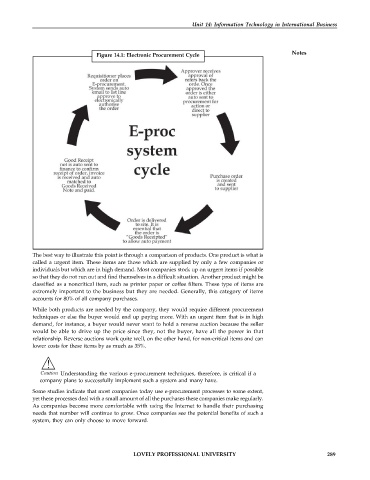
Figure 14.1: Electronic Procurement Cycle
The best way to illustrate this point is through a comparison of products. One product is what is
called a urgent item. These items are those which are supplied by only a few companies or
individuals but which are in high demand. Most companies stock up on urgent items if possible
so that they do not run out and find themselves in a difficult situation. Another product might be
classified as a noncritical item, such as printer paper or coffee filters. These type of items are
extremely important to the business but they are needed. Generally, this category of items
accounts for 80% of all company purchases.
While both products are needed by the company, they would require different procurement
techniques or else the buyer would end up paying more. With an urgent item that is in high
demand, for instance, a buyer would never want to hold a reverse auction because the seller
would be able to drive up the price since they, not the buyer, have all the power in that
relationship. Reverse auctions work quite well, on the other hand, for non-critical items and can
lower costs for these items by as much as 35%.
!
Caution Understanding the various e-procurement techniques, therefore, is critical if a
company plans to successfully implement such a system and many have.
Some studies indicate that most companies today use e-procurement processes to some extent,
yet these processes deal with a small amount of all the purchases these companies make regularly.
As companies become more comfortable with using the Internet to handle their purchasing
needs that number will continue to grow. Once companies see the potential benefits of such a
system, they can only choose to move forward.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 289